Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2021; 13(5): 386-415
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.386
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.386
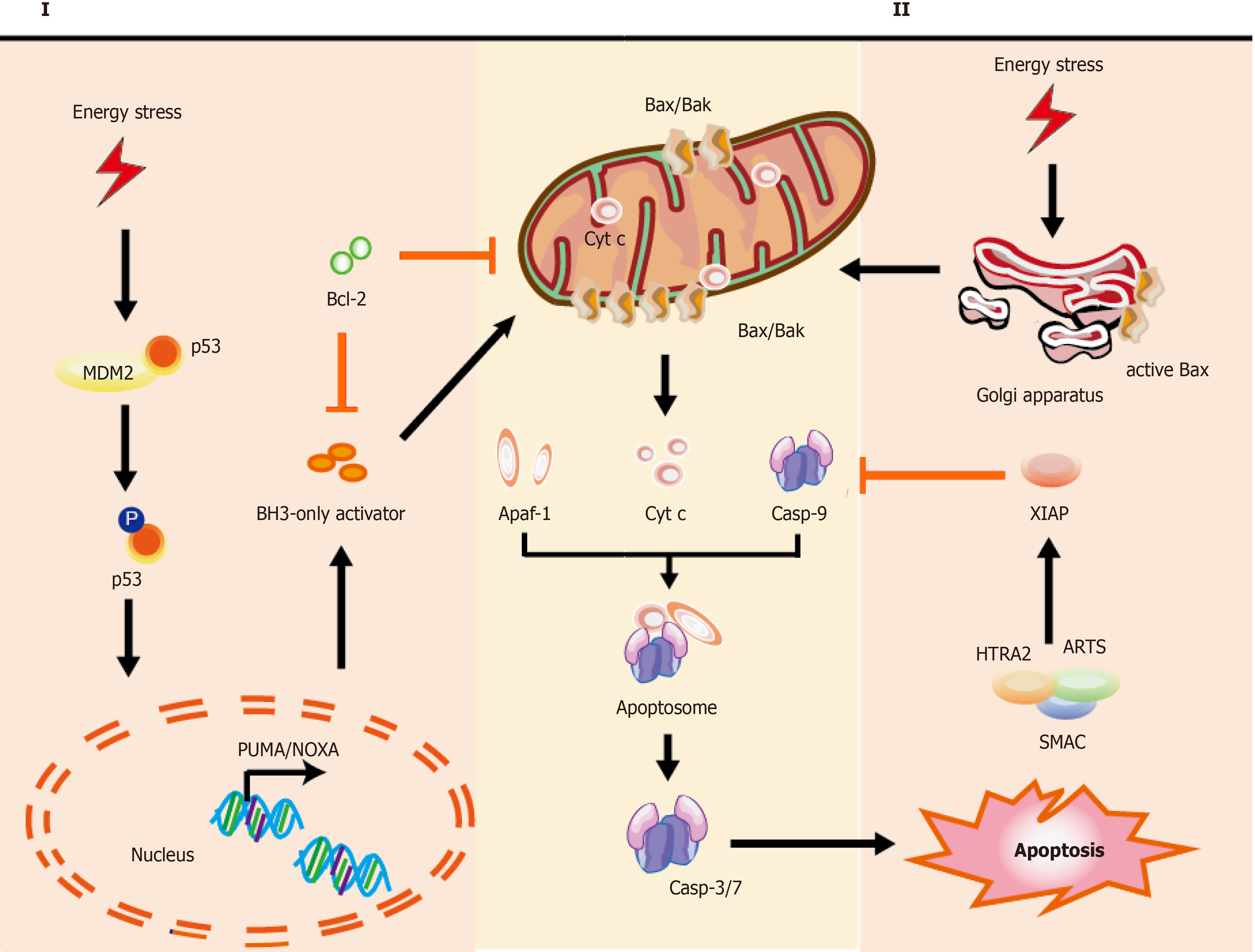
Figure 1 Mechanisms of intrinsic apoptotic pathways in stem cells.
Cell stress from various damage causes a rapid response leading to apoptosis via BH3-only activator (Way I) or active Bax directly from the Golgi (Way II) to the mitochondria, which subsequently induces a co-pathway [MOMP, cytochrome C (cyt C) releasing, etc.]. I: Stress inducers, such as DNA damage could stabilize and activate p53, which leads to p53 nuclear translocation. Subsequently, p53 exerts an impact on transcription of apoptotic genes via DNA-binding activity and its transcriptional activity (e.g., PUMA, NOXA, and Bax); II: Bax, which is monomeric in the cytoplasm, could be activated via stabilized p53 and active-Bax translocates from the Golgi to the mitochondrion. Once instigated with the apoptotic signals, active-Bax could lead to the alteration of MOMP, which undergoes dimerization and transfers to the OMM, so that relevant proteins (such as cyt C) are released into the cytosol usually confined in the intermembrane space. The released cyt C is involved in apoptosome formation via binding to the cytosolic Apaf-1. This complex recruits and activates initiator pro-casp-9, and then act-casp-9 activates downstream executor casp-3/-6/-7, leading to apoptotic cell death. In the cytoplasm, IAP antagonists (e.g., SMAC, ARTS, and HTRA2) could bind and suppress XIAP, causing the activation of casp-9 for the apoptotic pathway. The T-shaped lines indicate inhibitory interactions involved in this pathway, while the solid arrows indicate activating interactions. Bax: Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 associated X protein; OMM: Outer membrane permeabilization; MOMP: Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, cyt C: Cytochrome C; PUMA: p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis, NOXA: Pro-apoptotic BH3-only protein, also known as PMAIP1, phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1; Apaf-1: Apoptosis protease activating factor-1; IAP: Inhibitor of apoptosis; SMAC: Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase; ARTS: Apoptosis-related protein in the transforming growth factor-β signaling pathway; HTRA2: High-temperature-required protein A2.
- Citation: Hu XM, Zhang Q, Zhou RX, Wu YL, Li ZX, Zhang DY, Yang YC, Yang RH, Hu YJ, Xiong K. Programmed cell death in stem cell-based therapy: Mechanisms and clinical applications. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(5): 386-415
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i5/386.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.386