Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2021; 13(4): 317-330
Published online Apr 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i4.317
Published online Apr 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i4.317
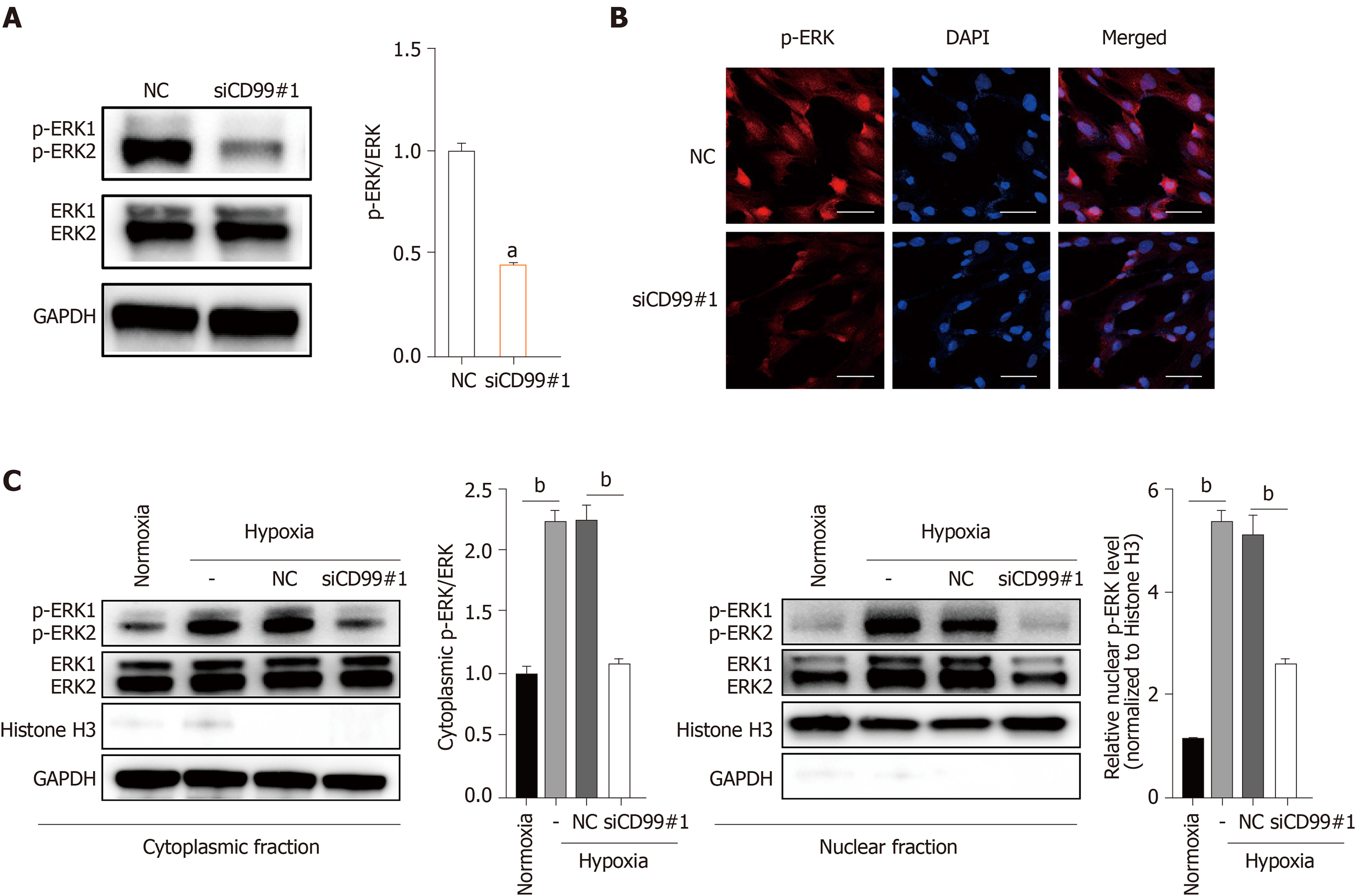
Figure 6 Hypoxia-induced CD99 expression modulates human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells proliferation via the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway.
A: Western blotting of phosphorylated (p)-ERK phosphorylation in human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hP-MSCs) exposed to hypoxia for 48 h and pretreated with siCD99#1; B: Immunofluorescence microscopy of (p-ERK) in hP-MSCs cultured under hypoxia for 48 h and pretreated with siCD99#1 (× 20 magnification; scale bars, 50 μm); C: Western blotting of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of hP-MSCs cultured under hypoxia for 48 h and pretreated with siCD99#1. p-ERK expression was normalized against that of ERK or histone H3. Data are means ± SD (n = 3). aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01. OD: Optical density.
- Citation: Feng XD, Zhu JQ, Zhou JH, Lin FY, Feng B, Shi XW, Pan QL, Yu J, Li LJ, Cao HC. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α–mediated upregulation of CD99 promotes the proliferation of placental mesenchymal stem cells by regulating ERK1/2. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(4): 317-330
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i4/317.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i4.317