Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2021; 13(2): 177-192
Published online Feb 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjSC.v13.i2.177
Published online Feb 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjSC.v13.i2.177
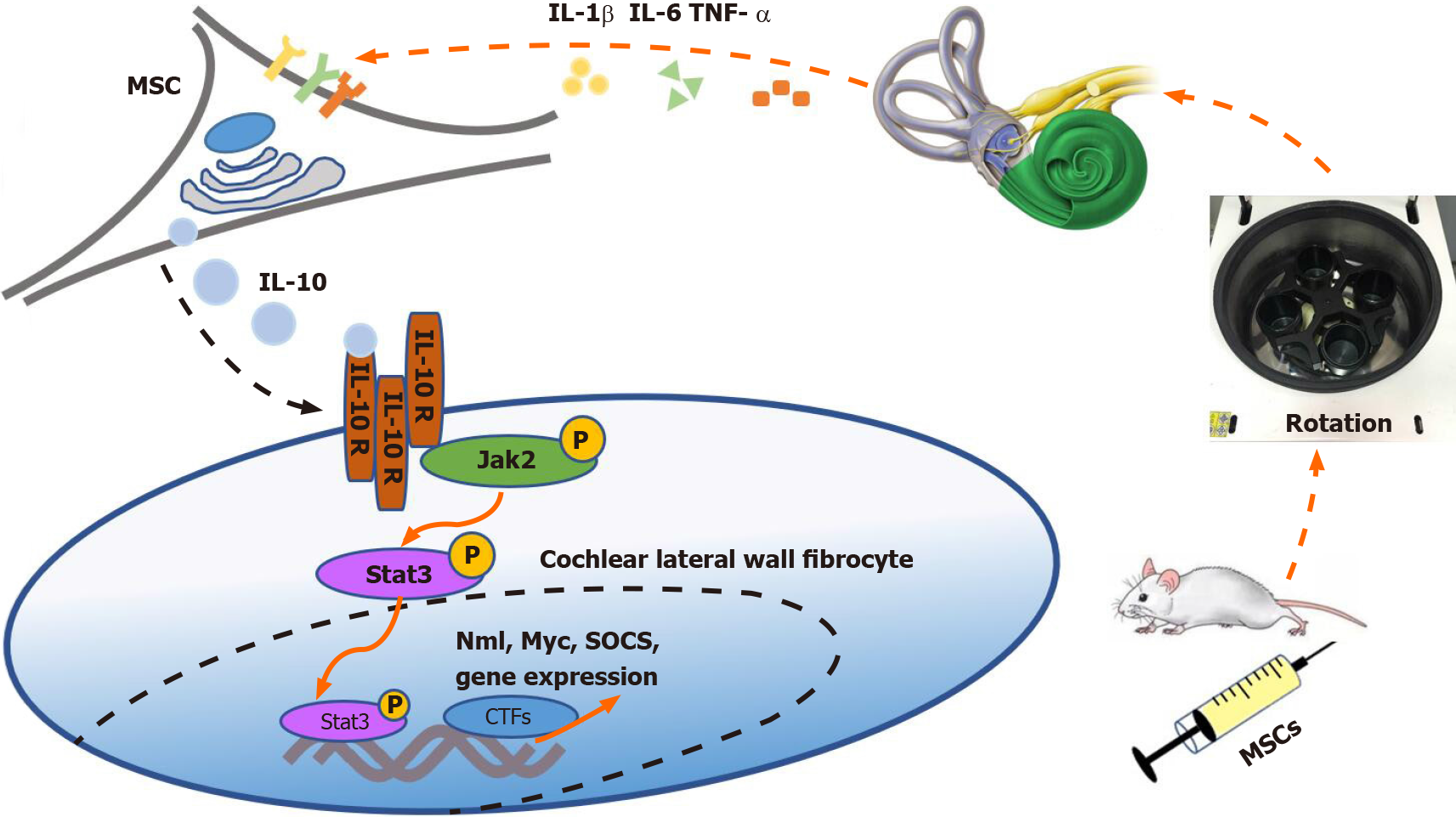
Figure 7 Proposed mechanism of action of mesenchymal stem cells in the vestibular microenvironment.
Mice were first prophylactically infused with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). After that, the motion sickness (MS) model was established at specified time points. At this time, pro-inflammatory cytokines in the vestibular environment of mice were released. MSCs were stimulated by these cytokines to secrete interleukin-10 (IL-10). Then, IL-10 receptors on fibrocytes in the cochlear lateral wall were triggered to activate the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Finally, the sensitivity of the vestibular cortex was reduced. IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; SOCS: Suppressor of cytokine signalling; Myc: Myelocytomatosis oncogene; CTFs: C-terminal fragments.
- Citation: Zhu HS, Li D, Li C, Huang JX, Chen SS, Li LB, Shi Q, Ju XL. Prior transfusion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can effectively alleviate symptoms of motion sickness in mice through interleukin 10 secretion. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(2): 177-192
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i2/177.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjSC.v13.i2.177