Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2021; 13(11): 1797-1812
Published online Nov 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i11.1797
Published online Nov 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i11.1797
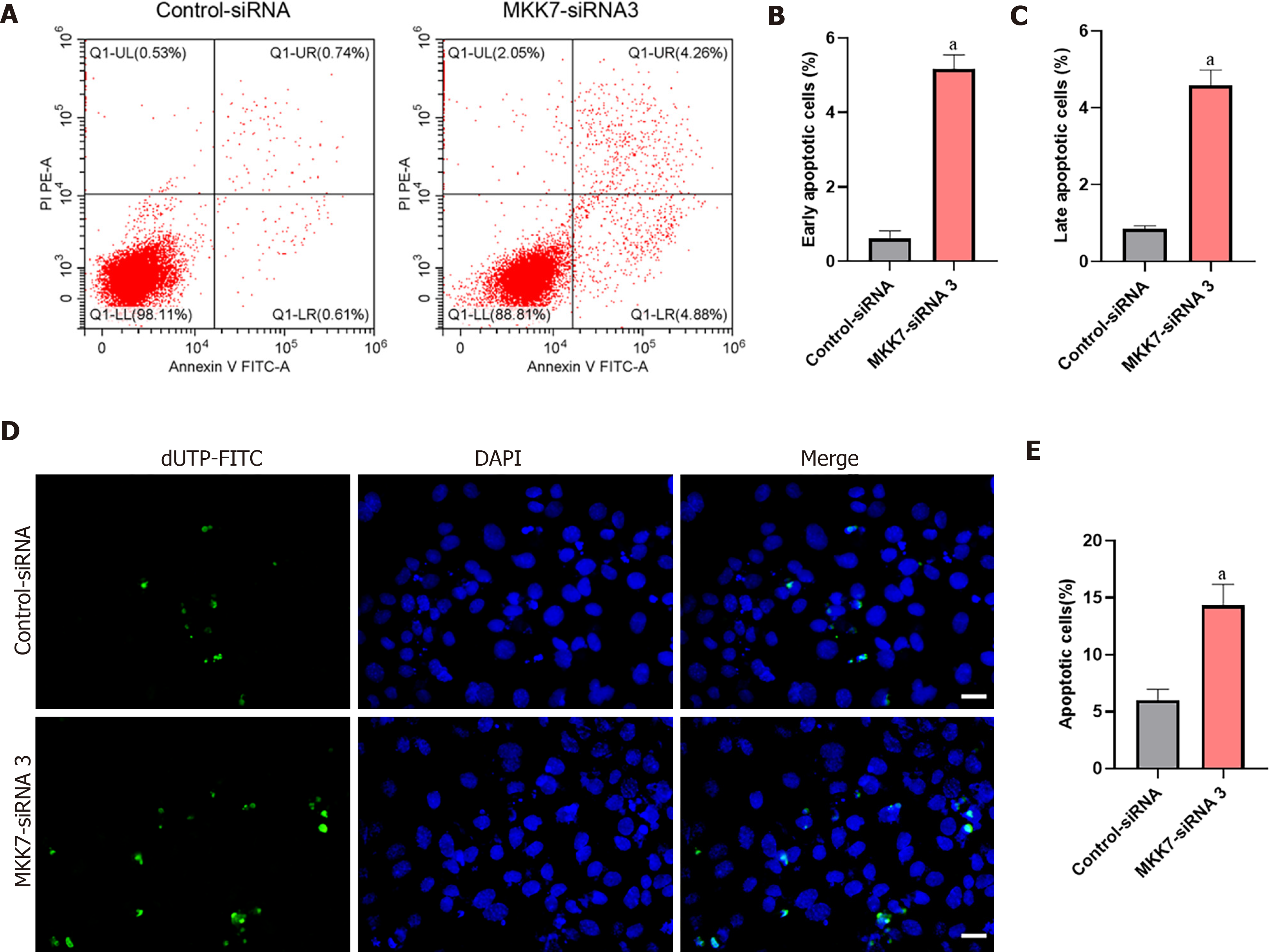
Figure 3 The influence of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7 knockdown on the apoptosis of human spermatogonial stem cells.
A-C: Flow cytometry and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) Annexin V analysis of the percentages of early (A and B) and late (A and C) apoptosis cells in human spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs) transfected with the Control-small interfering RNA (siRNA) and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7 (MKK7)siRNA 3; D and E: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase nick-end-labeling (TUNEL) assays of the percentages of TUNEL+ cells in human spermatogonial stem cells transfected with the Control-siRNA and MKK7-siRNA 3. Scale bars in D: 50 μm. aP < 0.05 denotes a significant difference between the MKK7-siRNA 3 and Control-siRNA groups. dUTP: Deoxyuridine 5’-triphosphate; DAPI: 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
- Citation: Huang ZH, Huang C, Ji XR, Zhou WJ, Luo XF, Liu Q, Tang YL, Gong F, Zhu WB. MKK7-mediated phosphorylation of JNKs regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of human spermatogonial stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(11): 1797-1812
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i11/1797.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i11.1797