Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2021; 13(11): 1667-1695
Published online Nov 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i11.1667
Published online Nov 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i11.1667
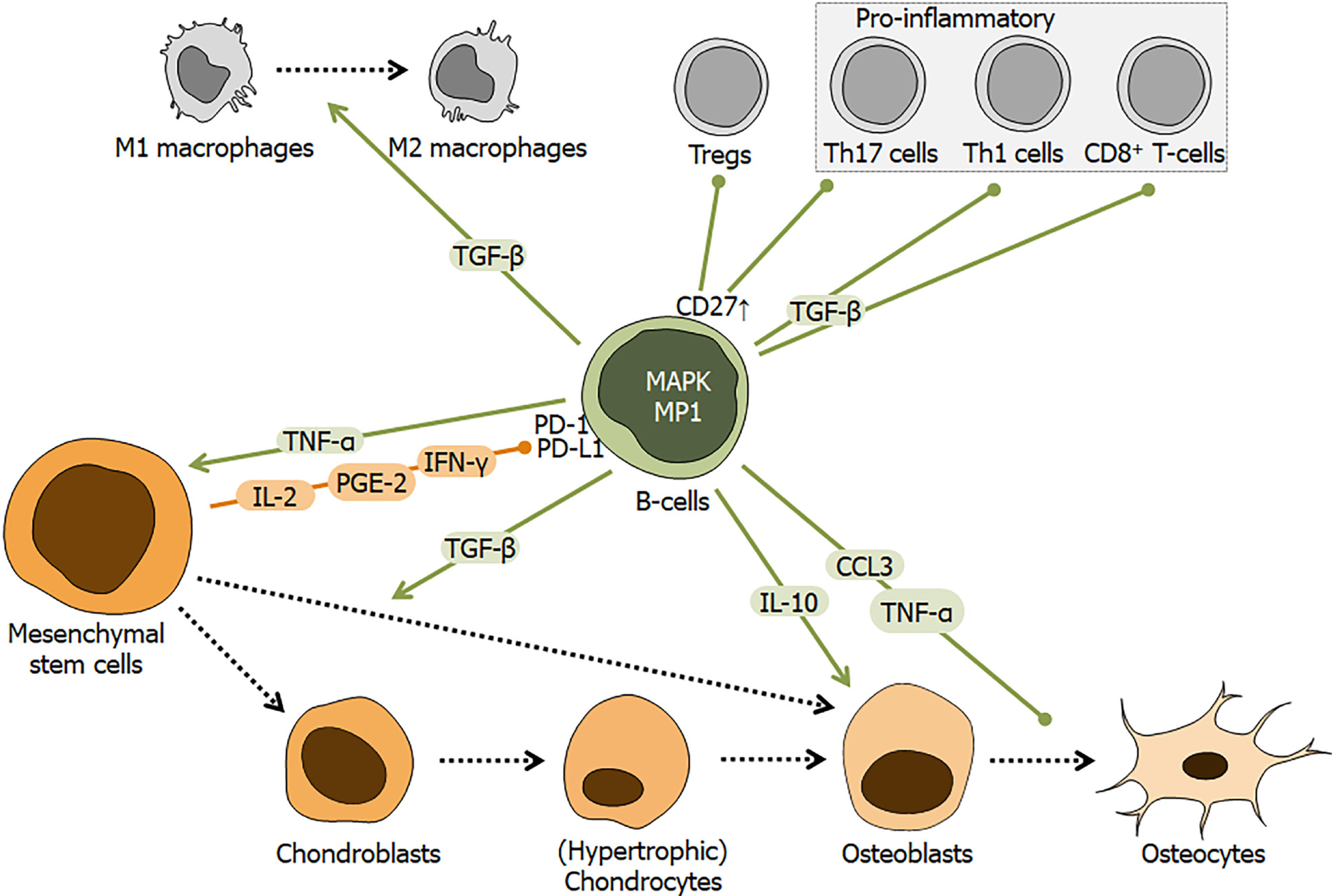
Figure 7 Schematic overview of the regulatory role of B-cells during fracture healing.
Fracture healing is affected by interactions between mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and B-cells. MSCs may affect B-cells by factors, e.g., interleukin 2 (IL-2), prostaglandin E2, and interferon gamma (IFN-γ), which interact with the programmed cell death 1 receptor and its ligand. Resulting in activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and its downstream target MEK partner 1, induces B-cells to secrete/release factors, e.g., tumor necrosis factor alpha, transforming growth factor beta, IL-10, and C-C-motif chemokine ligand 3. Colored arrows depict stimulation and blunt end lines inhibition. Dashed black arrows indicate differentiation processes. CD: Cluster of differentiation; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin; IFN: Interferon; CCL: C-C-motif chemokine ligand; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; Tregs: Regulatory T cells; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; PD-1: Programmed cell death 1; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand 1; MP1: MEK partner 1.
- Citation: Ehnert S, Relja B, Schmidt-Bleek K, Fischer V, Ignatius A, Linnemann C, Rinderknecht H, Huber-Lang M, Kalbitz M, Histing T, Nussler AK. Effects of immune cells on mesenchymal stem cells during fracture healing. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(11): 1667-1695
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i11/1667.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i11.1667