Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2021; 13(10): 1580-1594
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1580
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1580
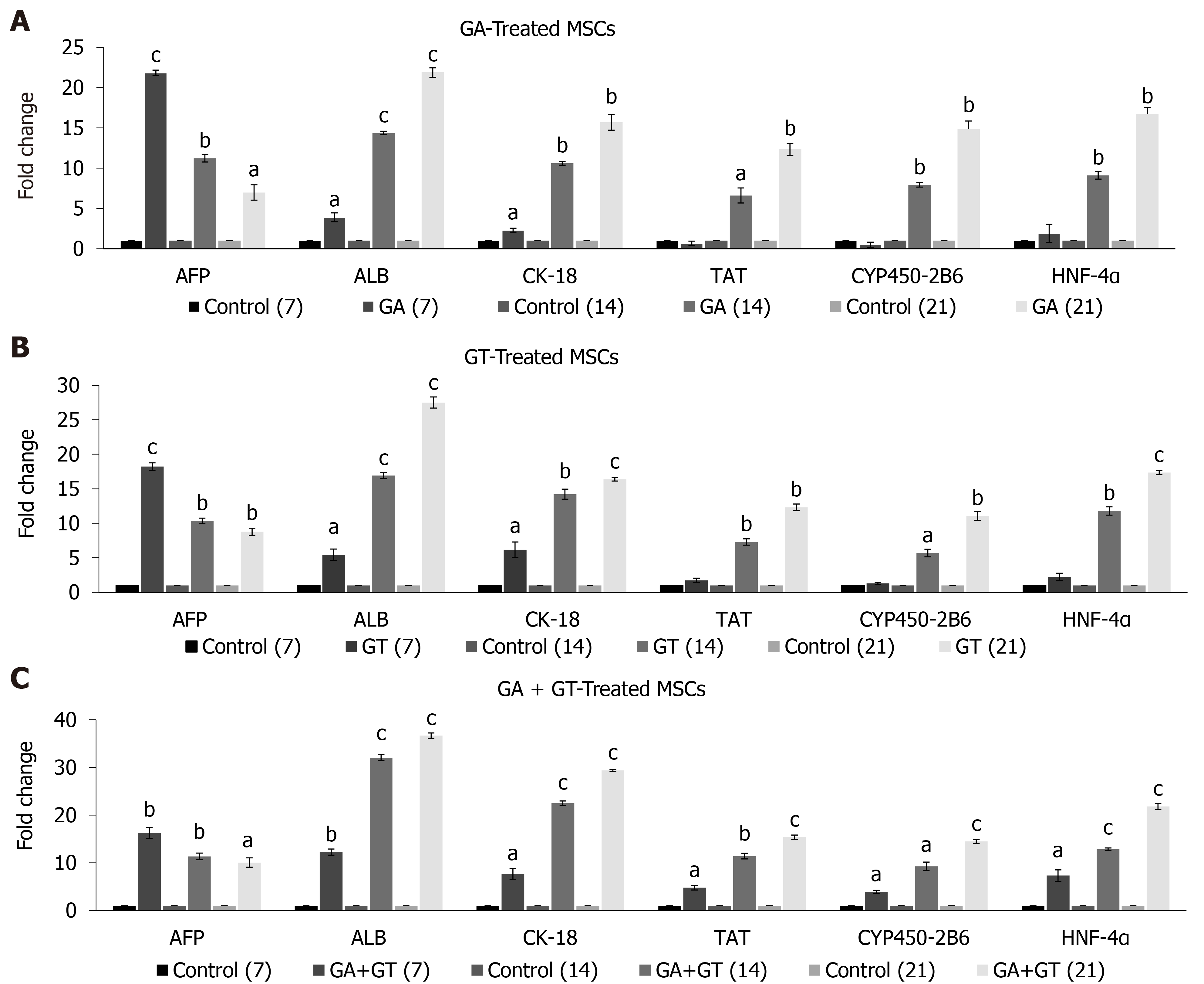
Figure 5 Expression of hepatic genes in human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells treated with glycyrrhizic acid, 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid, and their combination.
A and B: Glycyrrhizic acid (GA)- and 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid (GT)-treated mesenchymal stem cells showed significant expression of early hepatocyte marker AFP at all time points. Highest expression was observed at day 7 but it declined in a time-dependent manner. Significant expression levels of ALB and CK-18 were detected at all time points. Late hepatic markers, TAT, CYP450-2B6, and HNF-4α were not detectable at day 7 but were significantly up-regulated at day 14 and 21, as compared to the untreated control; C: GA + GT-treated MSCs revealed significant up-regulation of AFP at all time points. Highest expression was observed at day 7 but it declined with treatment time. Significant expression levels of ALB, CK-18, TAT, CYP450-2B6, and HNF-4α were observed at all time points and their expression increased with time of differentiation, as compared to the untreated control. Statistical analysis was conducted by independent sample t-test. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3); level of significance aP ≤ 0.05 (where aP ≤ 0.05, bP ≤ 0.01, and cP ≤ 0.001).
- Citation: Fatima A, Malick TS, Khan I, Ishaque A, Salim A. Effect of glycyrrhizic acid and 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid on the differentiation of human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(10): 1580-1594
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i10/1580.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1580