Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2021; 13(10): 1580-1594
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1580
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1580
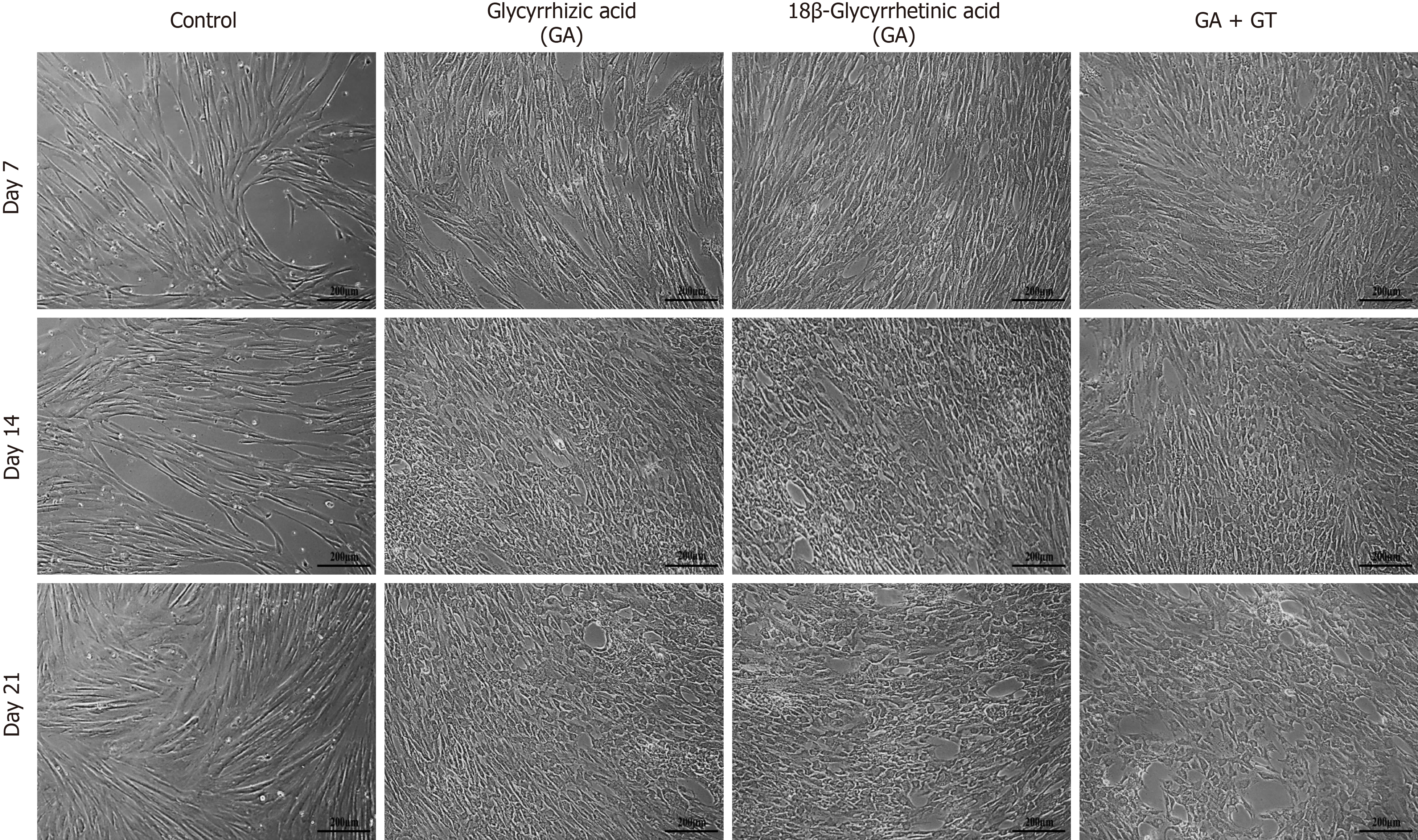
Figure 4 Morphological features of human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells treated with glycyrrhizic acid (GA), 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid (GT), and their combination (GA + GT).
At day 7, GA and GT treated MSCs became slightly shorter, flattened, and broader in appearance with retracted ends, while in the combination group, cells began to appear polygonal in shape. At day 14, changes were more apparent and cells progressively decreased in size and transformed into irregular or polygonal shape and by day 21, majority of the cells developed into more compact and polygonal morphology like that of hepatocytes exhibiting tight interactions between the cells in all treatment groups as compared to the untreated control. All images were taken under phase contrast at 10× magnification.
- Citation: Fatima A, Malick TS, Khan I, Ishaque A, Salim A. Effect of glycyrrhizic acid and 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid on the differentiation of human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(10): 1580-1594
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i10/1580.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1580