Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2021; 13(10): 1580-1594
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1580
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1580
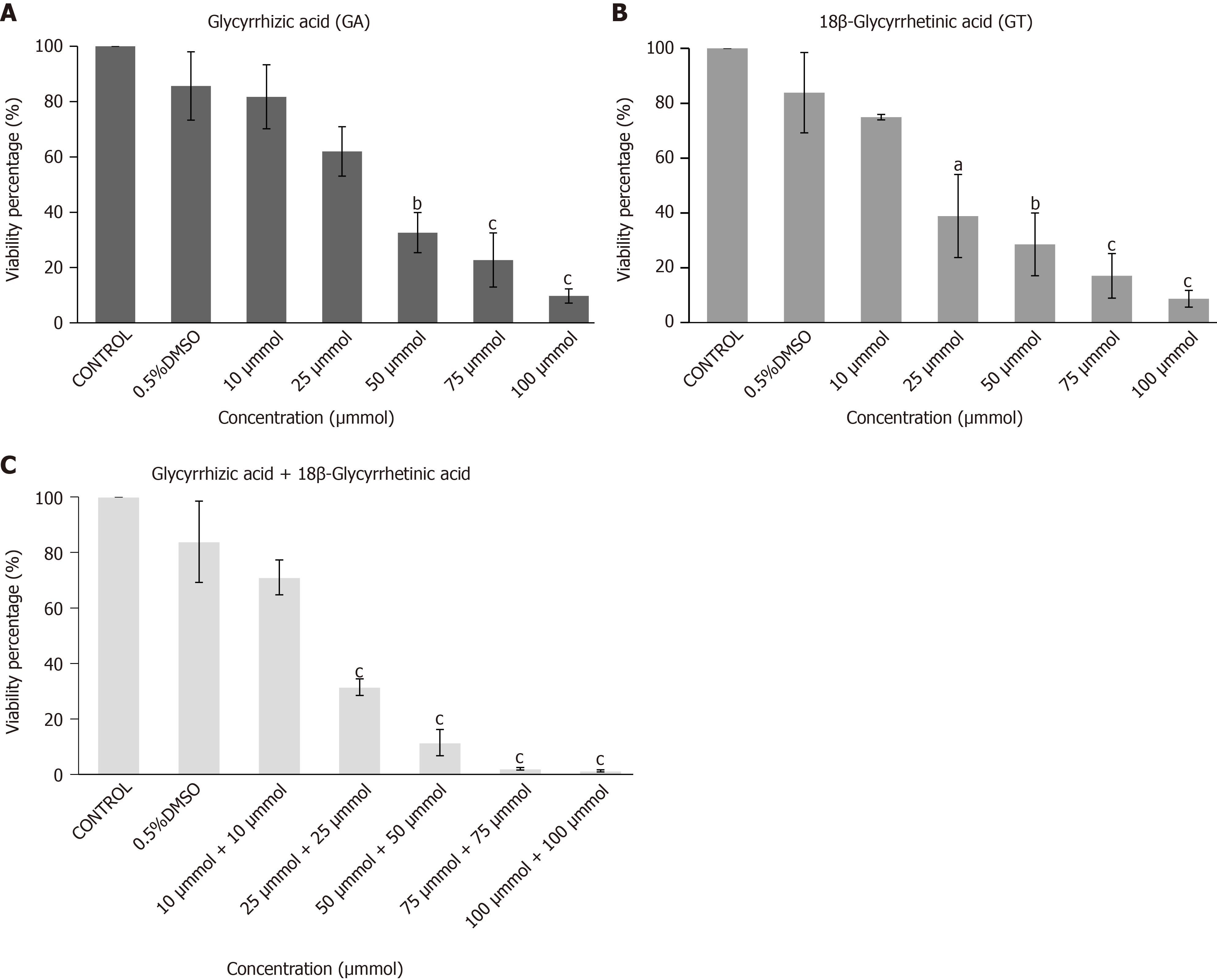
Figure 3 Cytotoxicity analysis of human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells by MTT Assay.
Bar graphs showing percent viability of human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells treated with A: glycyrrhizic acid (GA), B: 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid (GT), and C: their combination (GA + GT) at different concentrations. A decrease in percent (%) cell viability is observed with increasing concentrations of GA, GT and their combination. Statistical analysis was conducted by One-way ANOVA and Post-Hoc Bonferroni tests. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3); level of significance aP ≤ 0.05 (where aP ≤ 0.05, bP ≤ 0.01, and
- Citation: Fatima A, Malick TS, Khan I, Ishaque A, Salim A. Effect of glycyrrhizic acid and 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid on the differentiation of human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(10): 1580-1594
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i10/1580.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1580