Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2021; 13(10): 1417-1445
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1417
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1417
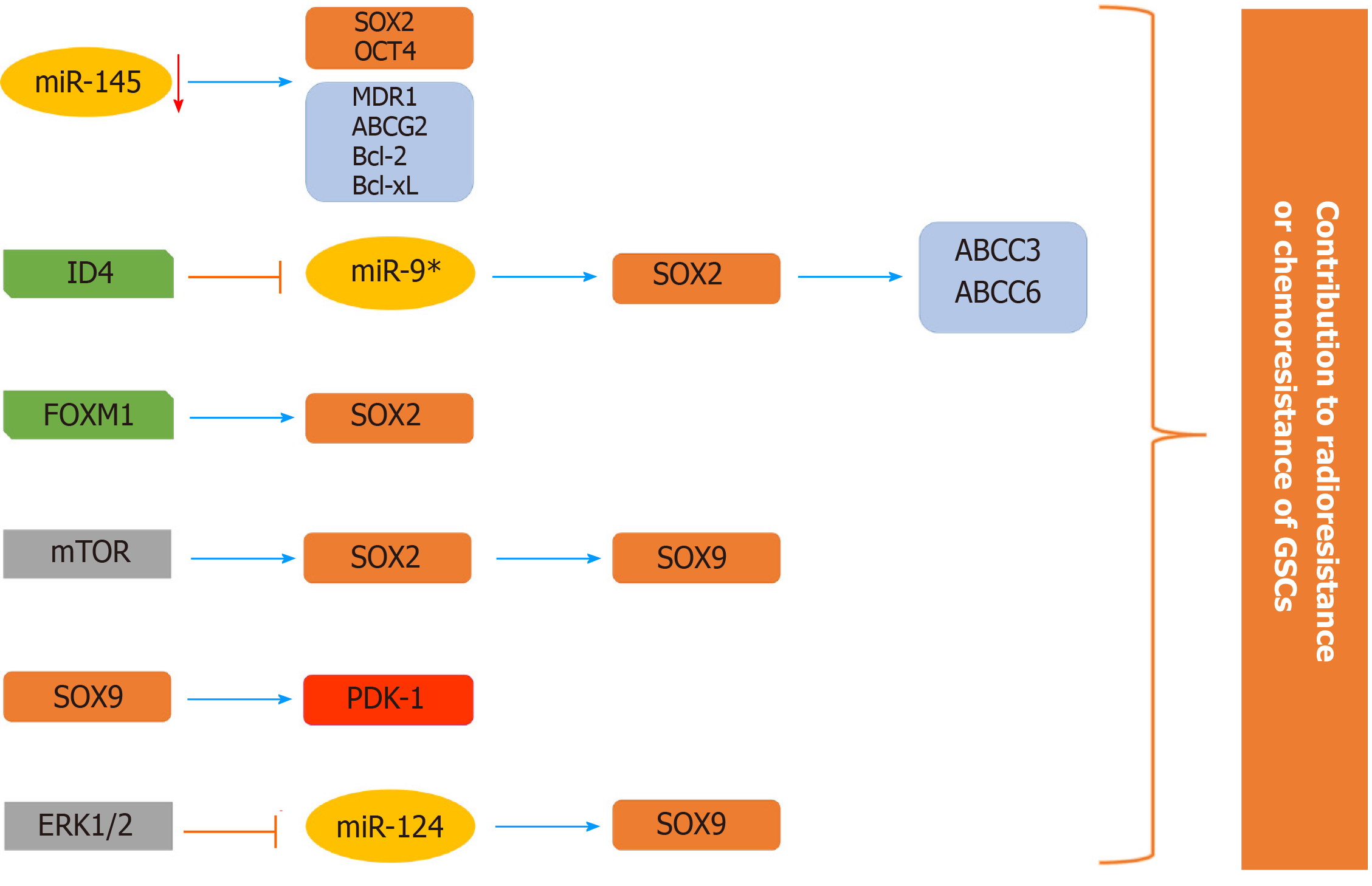
Figure 8 Schematic illustration of the involvement of SOX2 and SOX9 in the chemoresistance and radioresistance of glioma stem cells.
The expression of stemness-related transcription factor SOX2 is elevated in glioma stem cells (GSCs) through various mechanisms (decreased expression of miR-145 and miR-9* that directly target SOX2, direct transcriptional activation by Forkhead box M1 and through mammalian target of rapamycin signaling) contributing to chemo- and radioresistance of GSCs. SOX2 directly activates the expression of ABCC3 and ABCC6 transporters. mTOR signaling affects the SOX2/SOX9 axis, contributing to chemoresistance. The ERK1/2/miR-124/SOX9 axis and direct targeting of PDK1 (pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1) by SOX9 have a role in resistance to radiation and temozolomide, respectively. References are included in the main text. GSCs: Glioma stem cells; FOXM1: Forkhead box M1; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; PDK1: Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1.
- Citation: Stevanovic M, Kovacevic-Grujicic N, Mojsin M, Milivojevic M, Drakulic D. SOX transcription factors and glioma stem cells: Choosing between stemness and differentiation. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(10): 1417-1445
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i10/1417.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1417