Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2021; 13(10): 1417-1445
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1417
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1417
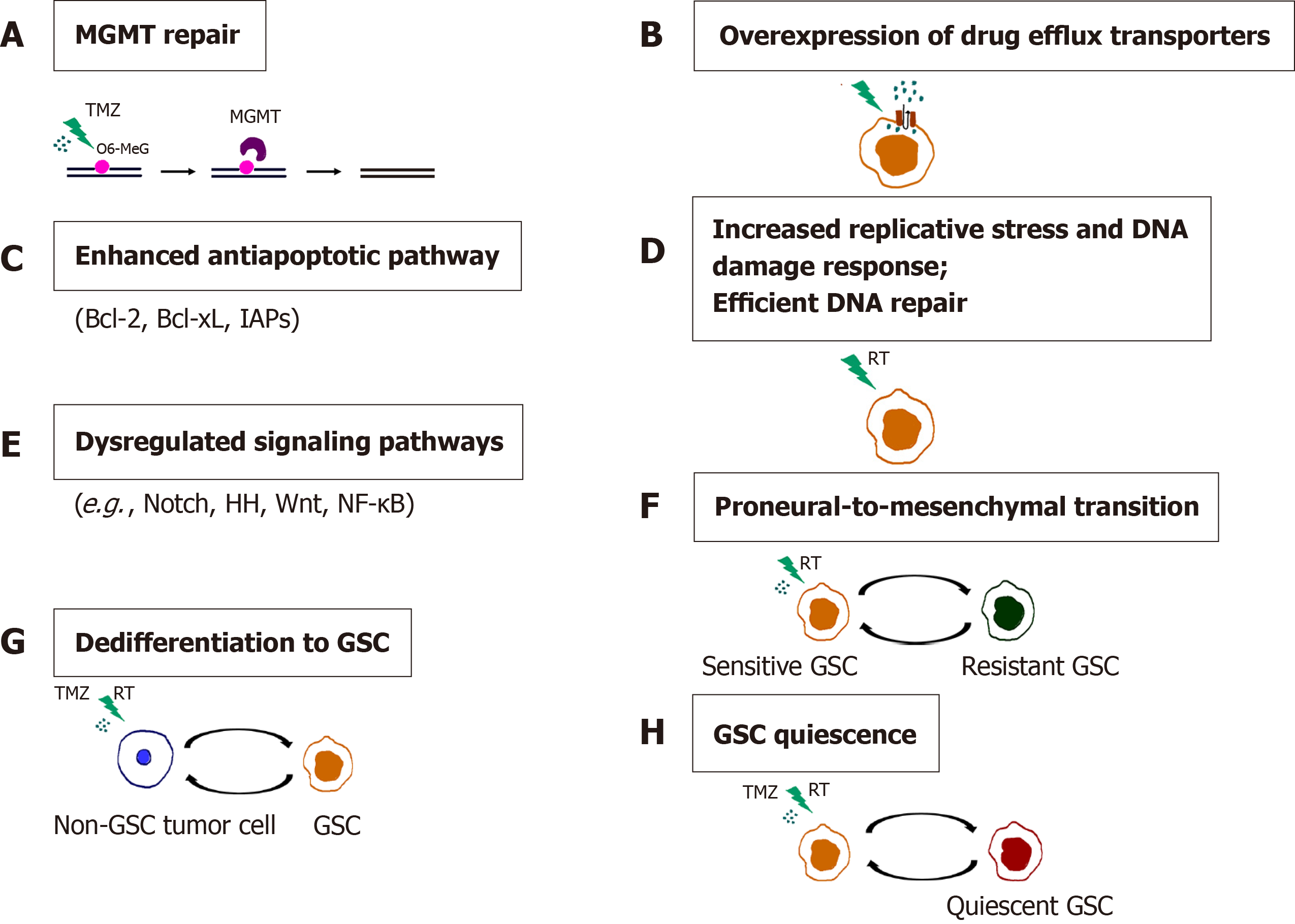
Figure 7 Mechanisms of chemo- and radioresistance of glioma stem cells.
A: O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) repair; B: Overexpression of drug efflux transporters; C: Enhanced antiapoptotic pathway; D: Increased replicative stress and DNA damage response. Efficient DNA repair; E: Dysregulated signaling pathways; F: Proneural-to-mesenchymal transition; G: Dedifferentiation to GSC; H: Glioma stem cells (GSC) quiescence. Resistance of GSCs to temozolomide is achieved through increased expression of MGMT, drug efflux transporters and antiapoptotic proteins. Replicative stress, constitutively active DNA damage response and efficient DNA repair confer radioresistance to GSCs. Aberrantly activated signaling pathways, the ability of non-GSC tumor cells to dedifferentiate, proneural-to-mesenchymal transition and the capacity of GSCs to become quiescent contribute to the chemo- and radioresistance of glioblastoma. References are included in the main text. RT: radiation; O6-MeG: O-6-methylguanine; GSC: Glioma stem cell; TMZ: Temozolomide.
- Citation: Stevanovic M, Kovacevic-Grujicic N, Mojsin M, Milivojevic M, Drakulic D. SOX transcription factors and glioma stem cells: Choosing between stemness and differentiation. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(10): 1417-1445
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i10/1417.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i10.1417