Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2020; 12(9): 1032-1049
Published online Sep 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i9.1032
Published online Sep 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i9.1032
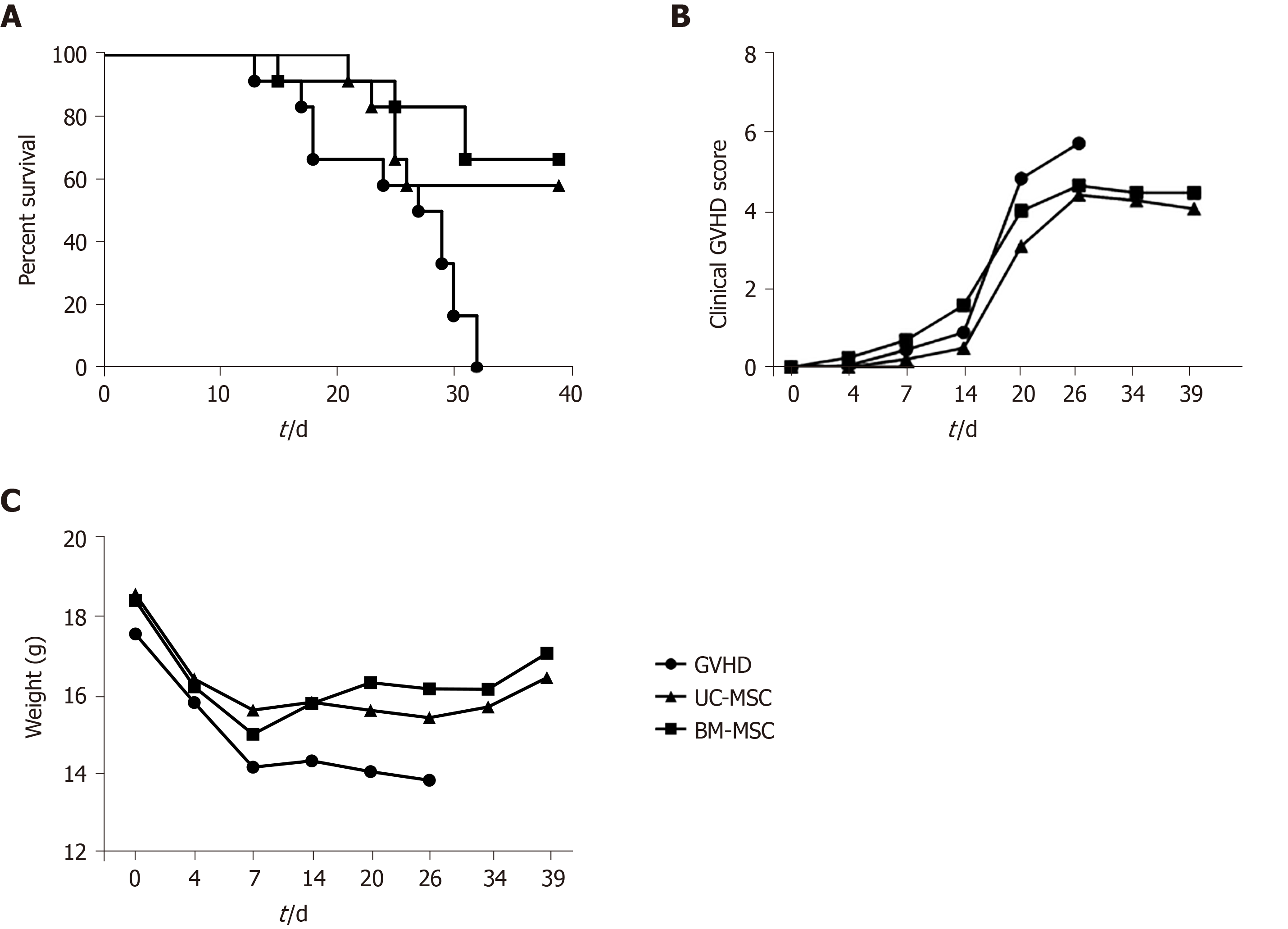
Figure 6 Inhibitory effects of mesenchymal stem cells therapy on graft-versus-host disease severity.
A-C: NOG mice were administered 200 cGy of total body irradiation before transplantation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (2 × 107). At days 0, 7 and 14 after transplantation, mice were administered with umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells or bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (1 × 105). All NOG mice were monitored for survival (A), clinical signs of graft-versus-host disease (B) and weight (C). BM-MSC: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells; GVHD: Graft-versus-host disease; UC-MSC: Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
- Citation: Song Y, Lim JY, Lim T, Im KI, Kim N, Nam YS, Jeon YW, Shin JC, Ko HS, Park IY, Cho SG. Human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord and bone marrow exert immunomodulatory effects in different mechanisms. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(9): 1032-1049
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i9/1032.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i9.1032