Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2020; 12(9): 1032-1049
Published online Sep 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i9.1032
Published online Sep 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i9.1032
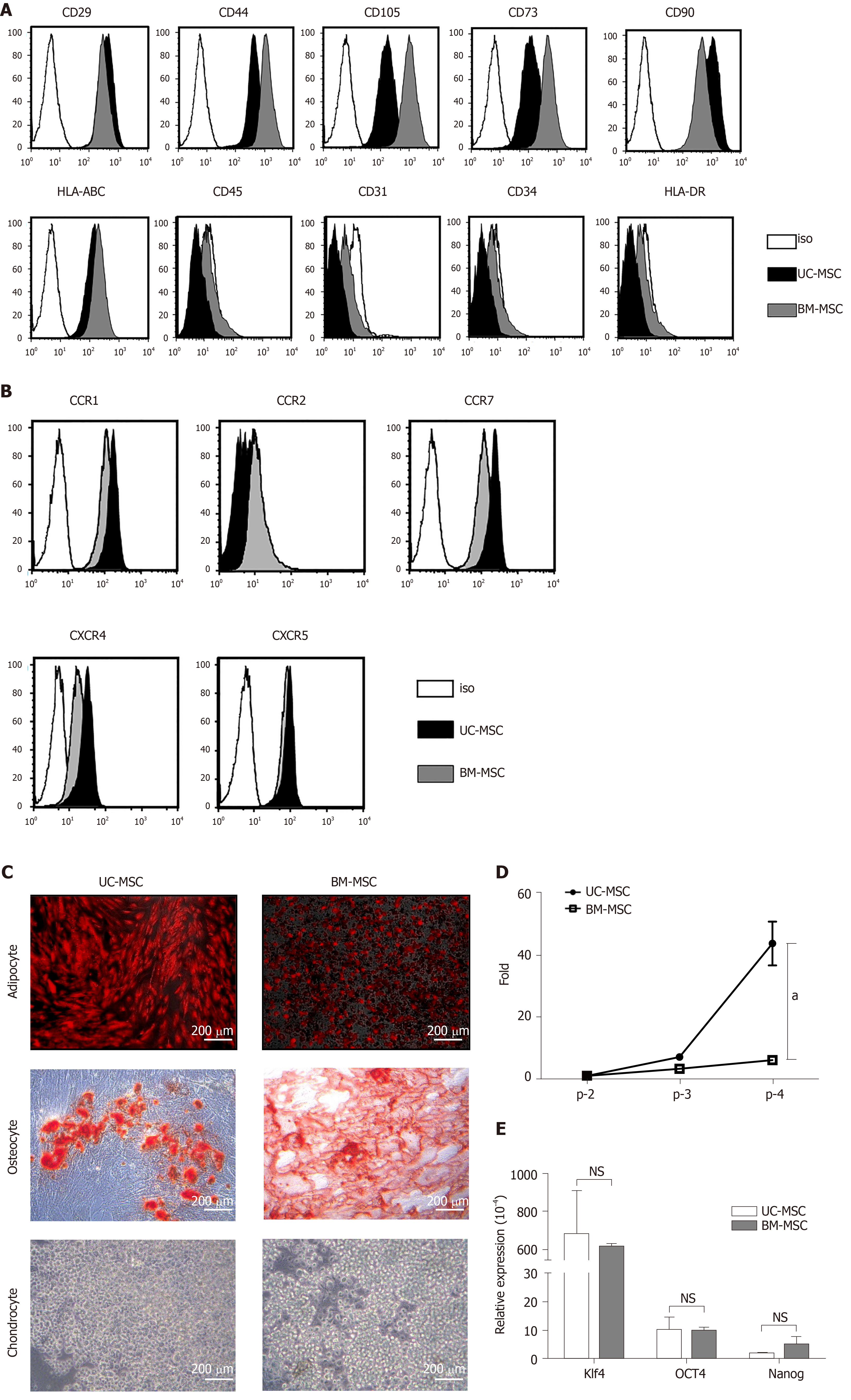
Figure 1 Characterization of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
A: Surface protein expression was analyzed using flow cytometry. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) were assessed at the fourth passage; B: Chemokine receptor expression was analyzed at passages 3–7 by flow cytometry; C: Representative images of umbilical cord-derived MSCs and bone marrow-derived MSCs differentiation into adipocytes (bone marrow-derived MSCs: day 7; umbilical cord-derived MSCs: day 21), chondrocytes (day 21) and osteocytes (day 14). Scale bars: 200 μm. Adipocytes were detected by goat anti-mouse FABP4 polyclonal antibody under a fluorescence microscope. Osteoblasts and chondrocytes were stained with Alizarin Red S and Alcian Blue, respectively and observed under a light microscope; D: Growth rate of MSCs at different passages; and E: Pluripotency transcription factor expression levels of cultured MSCs measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (target, GAPDH), D and E: Bone marrow-derived MSCs. Statistical analysis was performed by Student’s t-tests, aP < 0.05 vs indicated group. iso: Isotype; Klf4: Kruppel‐like factor 4; Nanog: Nanog homeobox; NS: No significance; OCT4: Octamer-binding transcription factor 4; UC-MSC: Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells; BM-MSCs: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
- Citation: Song Y, Lim JY, Lim T, Im KI, Kim N, Nam YS, Jeon YW, Shin JC, Ko HS, Park IY, Cho SG. Human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord and bone marrow exert immunomodulatory effects in different mechanisms. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(9): 1032-1049
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i9/1032.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i9.1032