Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2020; 12(8): 841-856
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.841
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.841
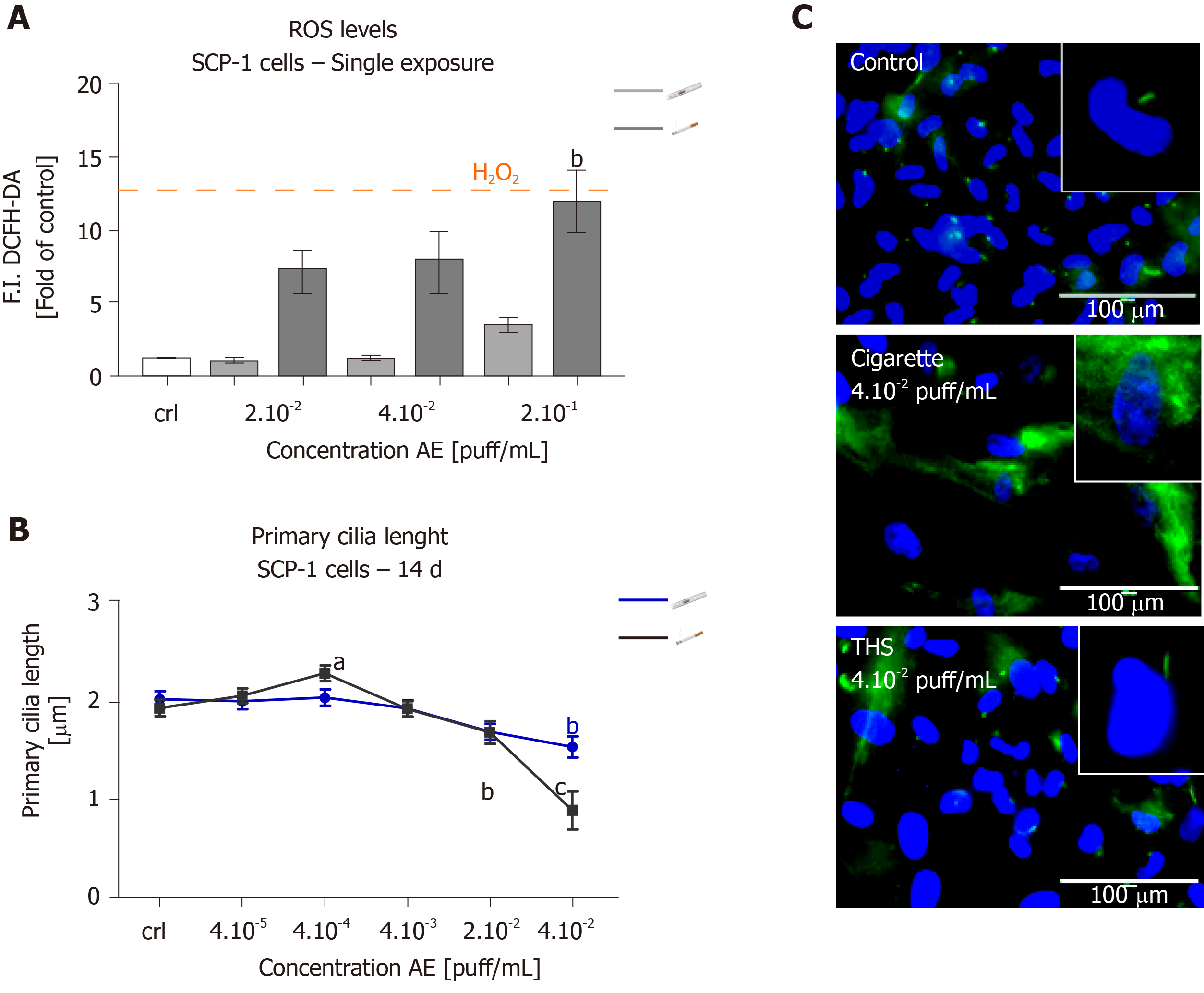
Figure 5 Tobacco heating systems induces less oxidative stress and causes less damage to primary cilia structures on bone cells precursor than conventional cigarettes.
SCP-1 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of aqueous extract (AE) from conventional cigarettes and tobacco heating systems (THS). ROS production was evaluated by DCFH-DA assay in SCP-1 cells. 0.01%v/v H2O2 was used as a positive control (A). Primary cilium length was quantified on day 14 by acetylated α-tubulin (green), and nuclei (blue) immunostaining (B). Representative immunostaining images of SCP-1 cells primary cilia after 14 days of chronic exposure to THS or conventional cigarettes AE (C) (scale bar 100 µm). Each measurement was conducted at least three independent times in triplicates. Data were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis H test followed by Dunn’s post-hoc tests. Data are represented as mean ± SE, and P values are classified as aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 for comparisons with untreated cells within AE type. AE: Aqueous extract.
- Citation: Aspera-Werz RH, Ehnert S, Müller M, Zhu S, Chen T, Weng W, Jacoby J, Nussler AK. Assessment of tobacco heating system 2.4 on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and primary human osteoblasts compared to conventional cigarettes. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(8): 841-856
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i8/841.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.841