Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2020; 12(8): 841-856
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.841
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.841
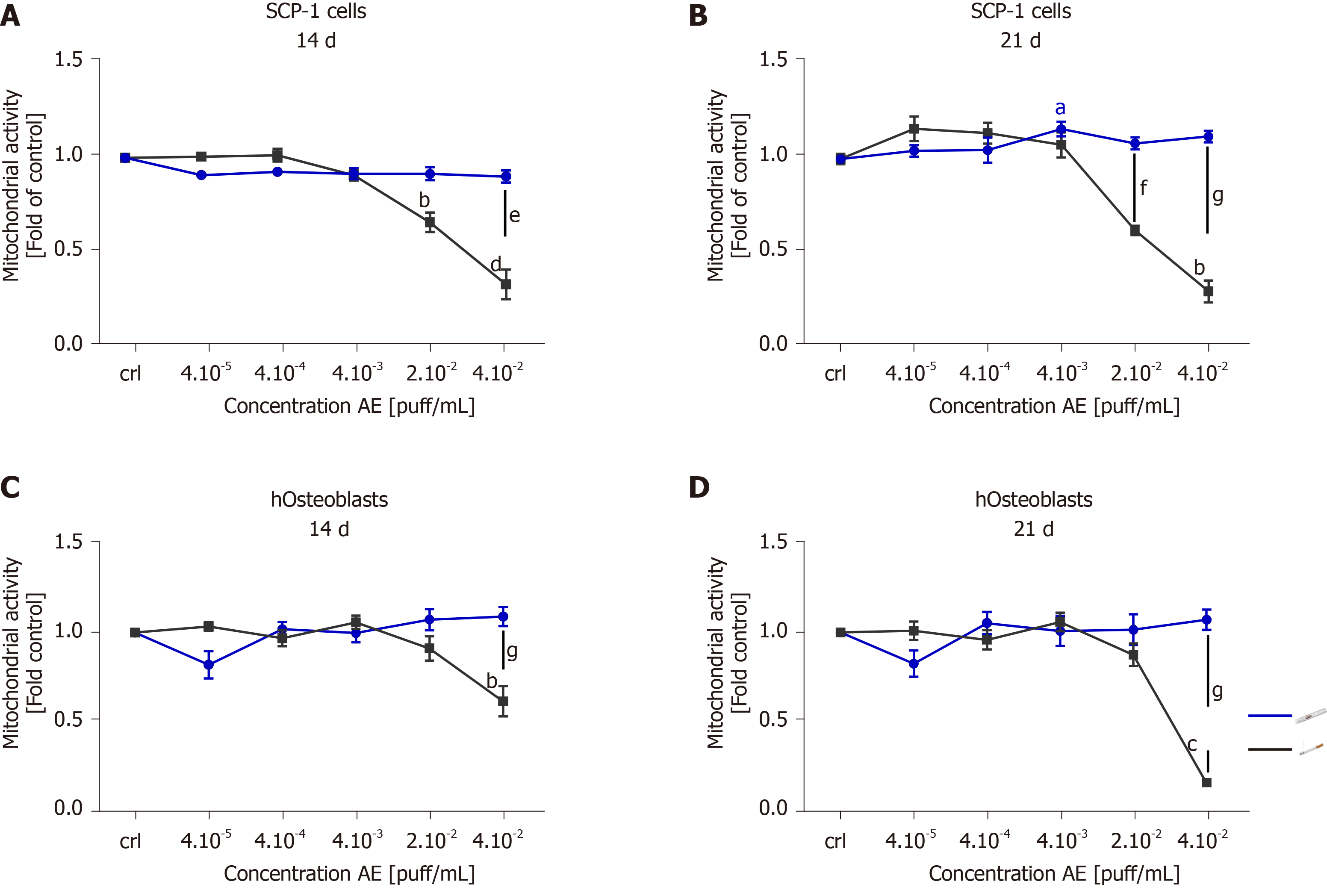
Figure 3 Tobacco heating systems is less toxic than conventional cigarettes after chronic exposure.
SCP-1 cells and primary human osteoblasts were osteogenically differentiated with increasing concentrations of aqueous extract (AE) from conventional cigarette and tobacco heating systems (THS) for 21 d. Cell viability was evaluated by resazurin conversion (mitochondrial activity) in SCP-1 cells (A, B) and primary human osteoblast (C, D) after 14 (A, C) and 21 d (B, D). Each measurement was conducted at least three independent times in triplicates. Data were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis H test followed by Dunn’s post-hoc test. Data are presented as mean ± SE. P values are classified as aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 for comparisons with untreated cells within AE type and as eP < 0.05, fP < 0.01, gP < 0.001 for comparisons of conventional cigarette with THS within the same concentration. AE: Aqueous extract.
- Citation: Aspera-Werz RH, Ehnert S, Müller M, Zhu S, Chen T, Weng W, Jacoby J, Nussler AK. Assessment of tobacco heating system 2.4 on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and primary human osteoblasts compared to conventional cigarettes. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(8): 841-856
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i8/841.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.841