Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2020; 12(8): 841-856
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.841
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.841
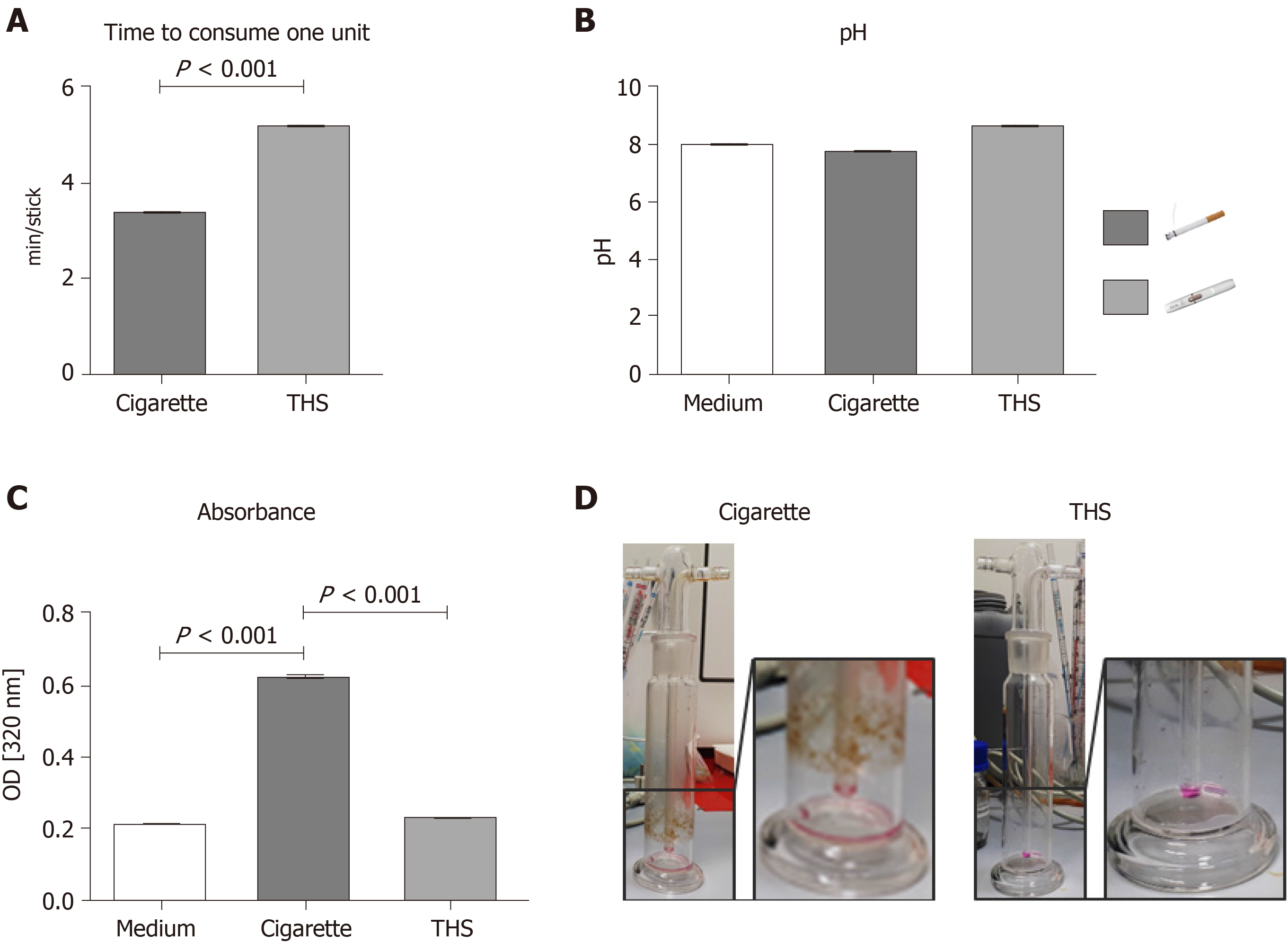
Figure 1 Tobacco heating systems and conventional cigarette aqueous extract characterization.
A: Time to consume one unit [cigarette or tobacco heating systems (THS) stick] measured in minutes; B: pH from the aqueous extract (AE) generated with conventional cigarettes or THS; C: Absorbance at 320 nm from the different fractions produced from conventional cigarette or THS; D: Representative picture of gas washing bottle after conventional cigarette or THS AE generation, respectively. Each measure was conducted with six independent AE for each condition in triplicates. Data were analyzed using the nonparametric Mann Whitney test or the Kruskal-Wallis H test followed by Dunn’s post-hoc tests. Data are presented as mean ± SE, and P < 0.001 for the comparison. THS: Tobacco heating systems.
- Citation: Aspera-Werz RH, Ehnert S, Müller M, Zhu S, Chen T, Weng W, Jacoby J, Nussler AK. Assessment of tobacco heating system 2.4 on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and primary human osteoblasts compared to conventional cigarettes. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(8): 841-856
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i8/841.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.841