Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2020; 12(7): 621-632
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i7.621
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i7.621
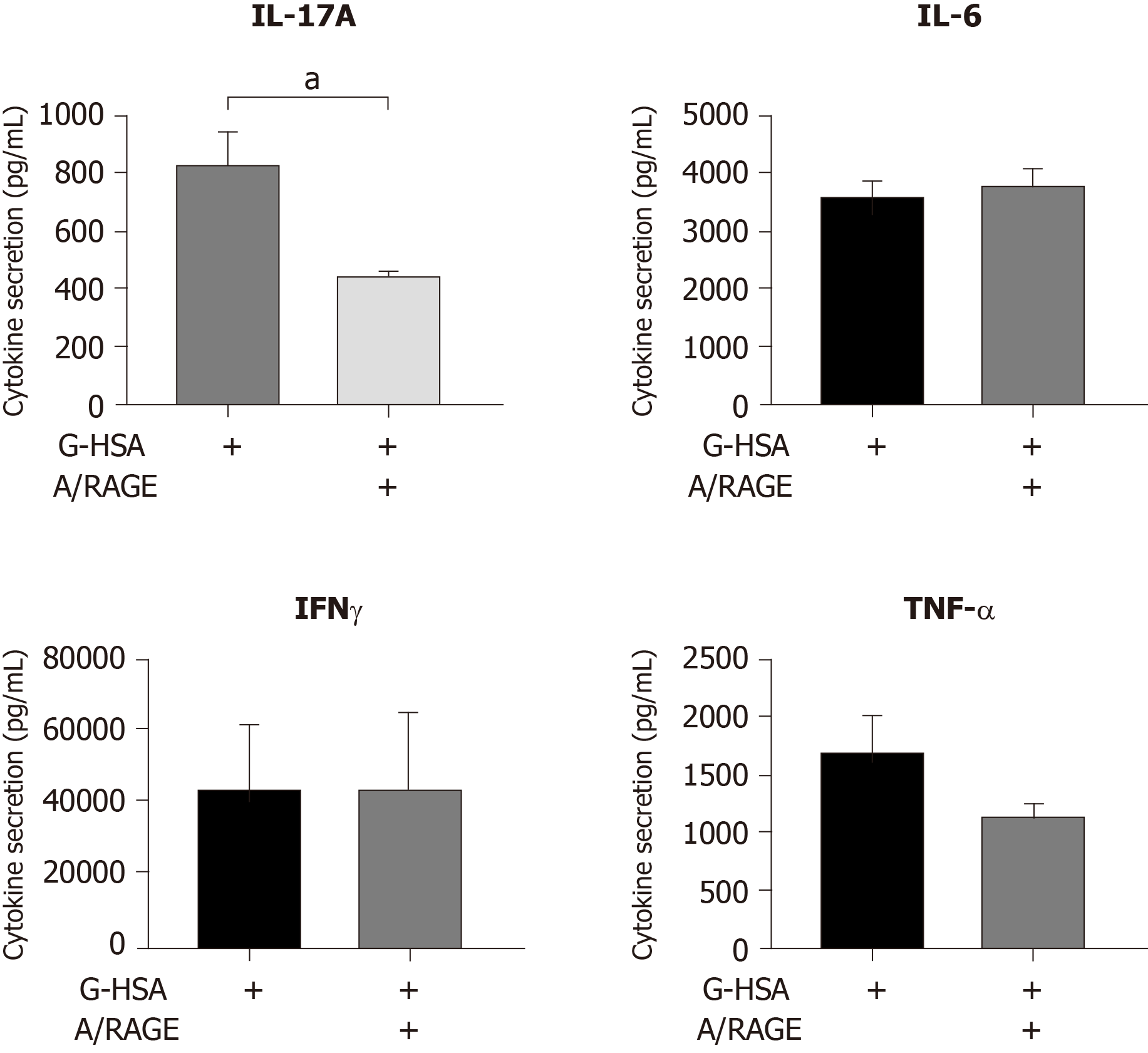
Figure 5 Inhibitory effects of anti-receptor for advanced glycated end products monoclonal antibody on interleukin 17A production.
Lean adipose-derived stem cells (ASC) were co-cultured with mononuclear cells (MNC) at the 1:5 ASC to MNC cell ratio, in the presence of 1% glycated human serum albumin for 48 h, phytohemagglutinin A was added. Anti-receptor for advanced glycated end products monoclonal antibody was added at a concentration of 20 µg/mL. ELISA were performed to measure interleukin (IL)-17A, interferon gamma, tumor necrosis factor alpha and IL-6 secretion. Bars represent the mean ± SE of 5 independent experiments performed in triplicates. aP < 0.05, as obtained by paired t tests. ASC: Adipose-derived stem cells; MNC: Mononuclear cells; G-HSA: Glycated human serum albumin; PHA: Phytohemagglutinin A; RAGE: Receptor for advanced glycated end products; mAb: Monoclonal antibody; IL: Interleukin; IFNγ: Interferon gamma; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
- Citation: Pestel J, Robert M, Corbin S, Vidal H, Eljaafari A. Involvement of glycated albumin in adipose-derived-stem cell-mediated interleukin 17 secreting T helper cell activation. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(7): 621-632
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i7/621.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i7.621