Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2020; 12(7): 562-584
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i7.562
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i7.562
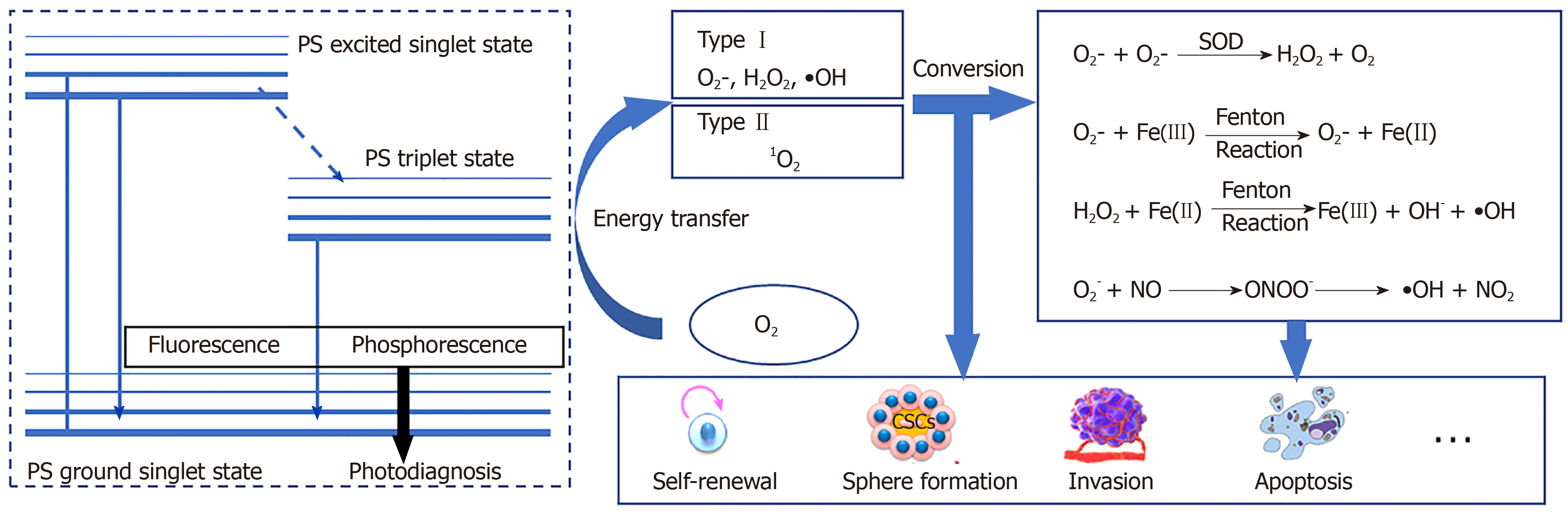
Figure 1 The process of reactive oxygen species production and transformation in cancer stem cells.
A: The photosensitizer is activated from the ground singlet state to the excited singlet state and triplet state. The excited singlet state and triplet state can release energy through fluorescence and phosphorescence, or transfer energy to generate various reactive oxygen species (ROS); B: The mutual transformation of ROS in vivo. These ROS all affect the self-renewal, sphere formation, invasion, and apoptosis of cancer stem cells. PS: Photosensitizer; H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; •OH: Hydroxyl radicals; OH−: Hydroxyl; NO: Nitric oxide; ONOO−: Peroxynitrite anion; NO2: Nitrogen dioxide.
- Citation: Zhang ZJ, Wang KP, Mo JG, Xiong L, Wen Y. Photodynamic therapy regulates fate of cancer stem cells through reactive oxygen species. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(7): 562-584
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i7/562.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i7.562