Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2020; 12(6): 500-513
Published online Jun 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i6.500
Published online Jun 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i6.500
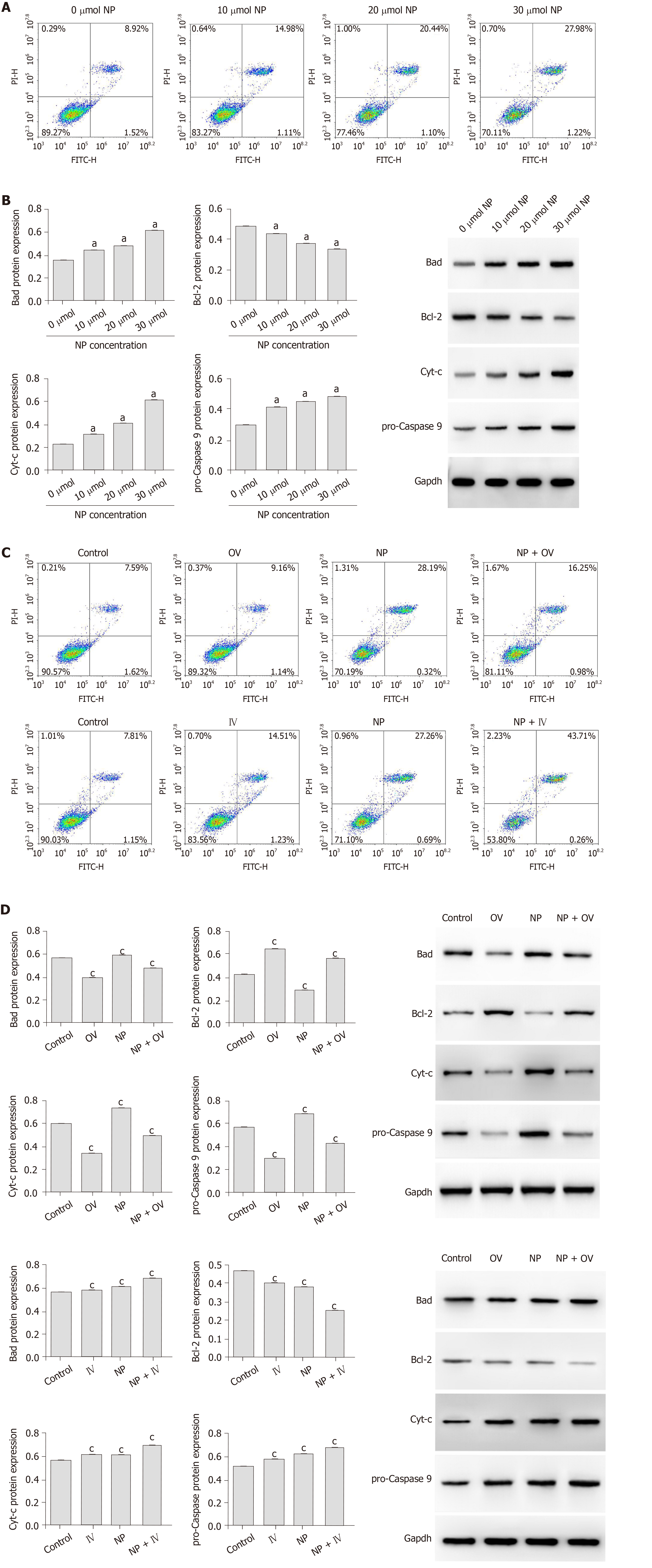
Figure 3 Effect of nonylphenol on apoptosis and oxidative stress in spermatogonial stem cells.
A: Detection of apoptosis by flow cytometry; B: Western blot of the protein expression of Bad, Bcl-2, Cyt-c, and pro-Caspase 9. The results are presented as the mean ± standard deviation, n = 3. aP < 0.05 vs 0 μmol NP; C: Effect of nonylphenol on spermatogonial stem cell apoptosis after mammalian target of rapamycin activation or inhibition; D: Expression of apoptosis-related protein detected by western blot. The results are presented as the mean ± standard deviation, n = 3. cP < 0.05 vs control. NP: Nonylphenol; Control: Control group, not subjected to any activator or inhibitor; NP: Nonylphenol group; OV: Mammalian target of rapamycin activator group; OV + NP: OV + NP group.
- Citation: Lei JH, Yan W, Luo CH, Guo YM, Zhang YY, Wang XH, Su XJ. Cytotoxicity of nonylphenol on spermatogonial stem cells via phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(6): 500-513
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i6/500.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i6.500