Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2020; 12(2): 139-151
Published online Feb 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i2.139
Published online Feb 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i2.139
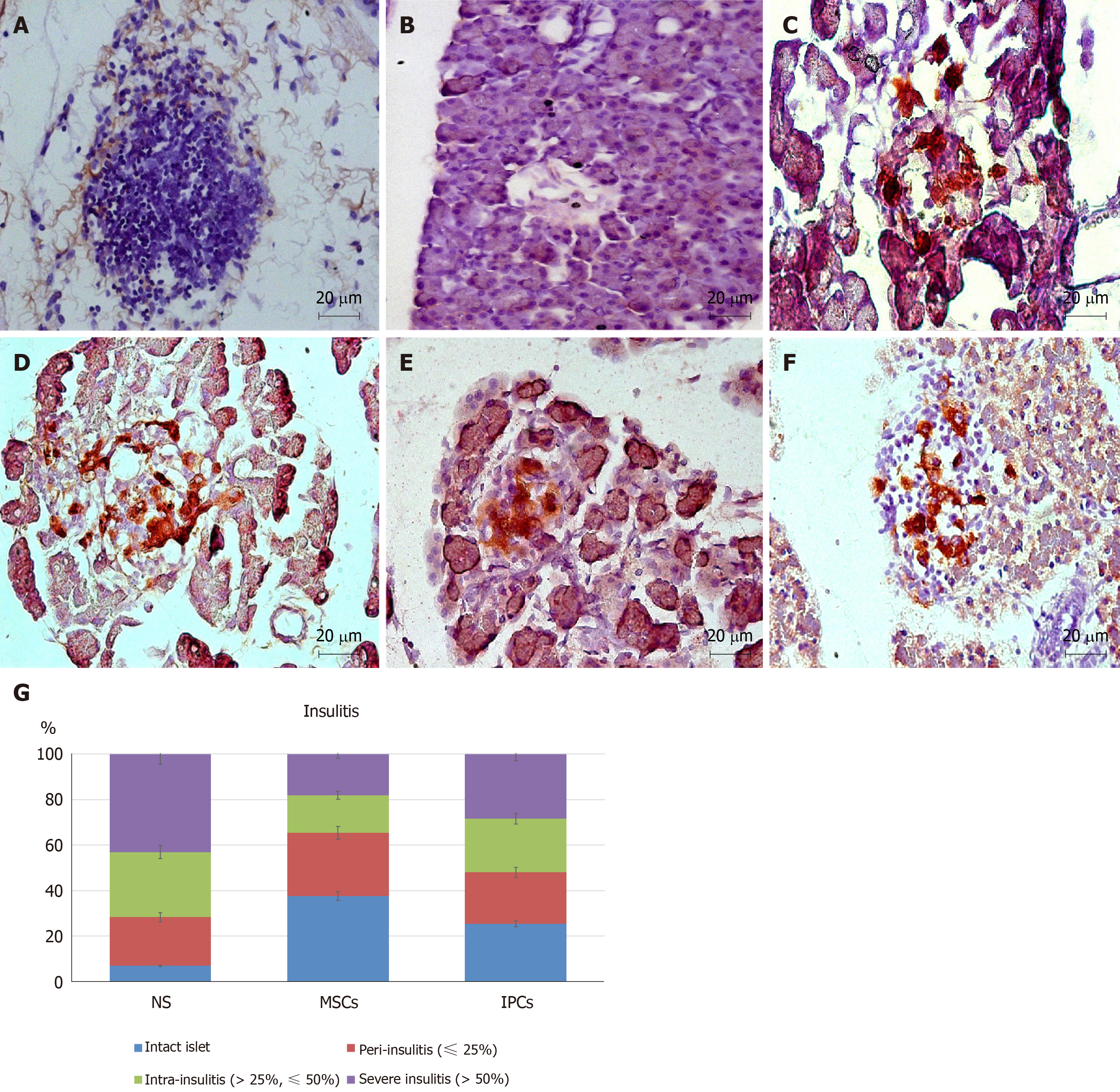
Figure 6 Comparison of pancreatic immunohistochemistry staining in the different treatment groups of diabetic rats.
A, B: Pancreas of rats from the normal saline (NS) treatment group (40 ×); C, D: Pancreas of rats from the mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) treatment group (40 ×); E, F: Pancreas of rats from the insulin-producing cell (IPC) treatment group (40 ×); G: Intact islets: 0% lymphocyte infiltration, peri-insulitis: < 25% lymphocyte infiltration, intra-insulitis: 25%-50% lymphocyte infiltration, severe insulitis: > 50% lymphocyte infiltration. The percentage of islets free from lymphocyte infiltration was about 7% in rats from the NS treatment group but was 38% in rats from the MSC treatment group (aP < 0.05). Only 18% of the islets from MSC-treated rats showed severe insulitis compared with 43% of rats from the NS treatment group (aP < 0.05). NS: normal saline treatment group; MSCs: Undifferentiated Wharton’s jelly-MSCs treatment group; IPCs: Insulin-producing cells treatment group; Red: Human cell nucleus; Brown: Human insulin.
- Citation: Hsiao CY, Chen TH, Huang BS, Chen PH, Su CH, Shyu JF, Tsai PJ. Comparison between the therapeutic effects of differentiated and undifferentiated Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(2): 139-151
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i2/139.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i2.139