Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2020; 12(2): 123-138
Published online Feb 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i2.123
Published online Feb 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i2.123
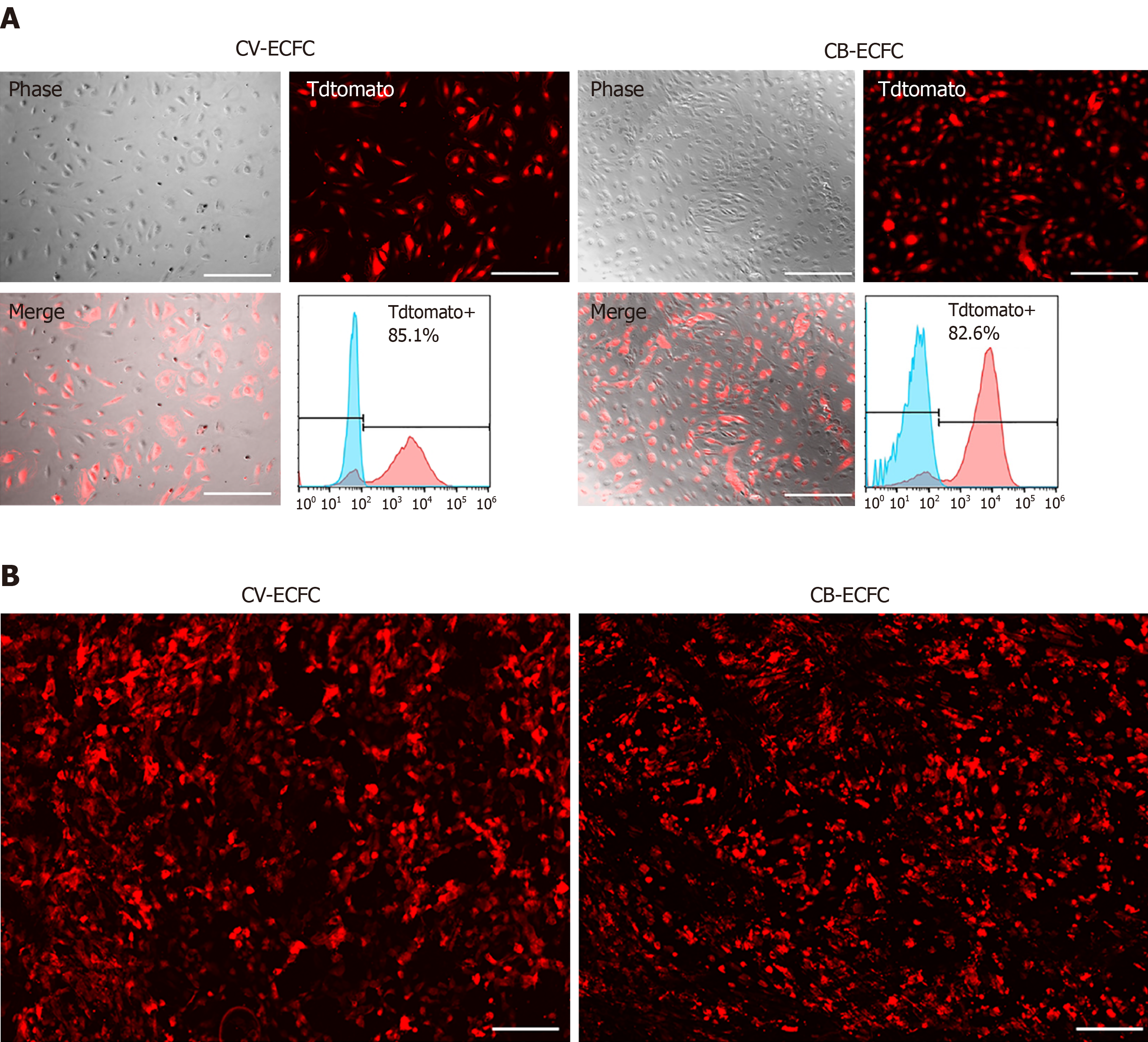
Figure 5 Chorionic villus endothelial colony-forming cells can be transduced by lentiviral vector and are compatible with a small intestinal submucosa scaffold.
A: Representative images of chorionic villus endothelial colony-forming cells (CV-ECFCs) and cord blood-derived ECFCs (CB-ECFCs) transduced with a pCCLc-MNDU3-LUC-PGK-Tomato-WPRE lentiviral vector. Flow cytometric analysis showed a transduction rate of 85.1% and 82.8%, respectively; B: tdTomato lentiviral vector-transduced CV-ECFCs (left panel) and CB-ECFCs (right panel) seeded onto a small intestinal submucosa extracellular matrix scaffold, showing adherence. Scale bar = 100 µm.
- Citation: Gao K, He S, Kumar P, Farmer D, Zhou J, Wang A. Clonal isolation of endothelial colony-forming cells from early gestation chorionic villi of human placenta for fetal tissue regeneration. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(2): 123-138
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i2/123.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i2.123