Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2020; 12(12): 1652-1666
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1652
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1652
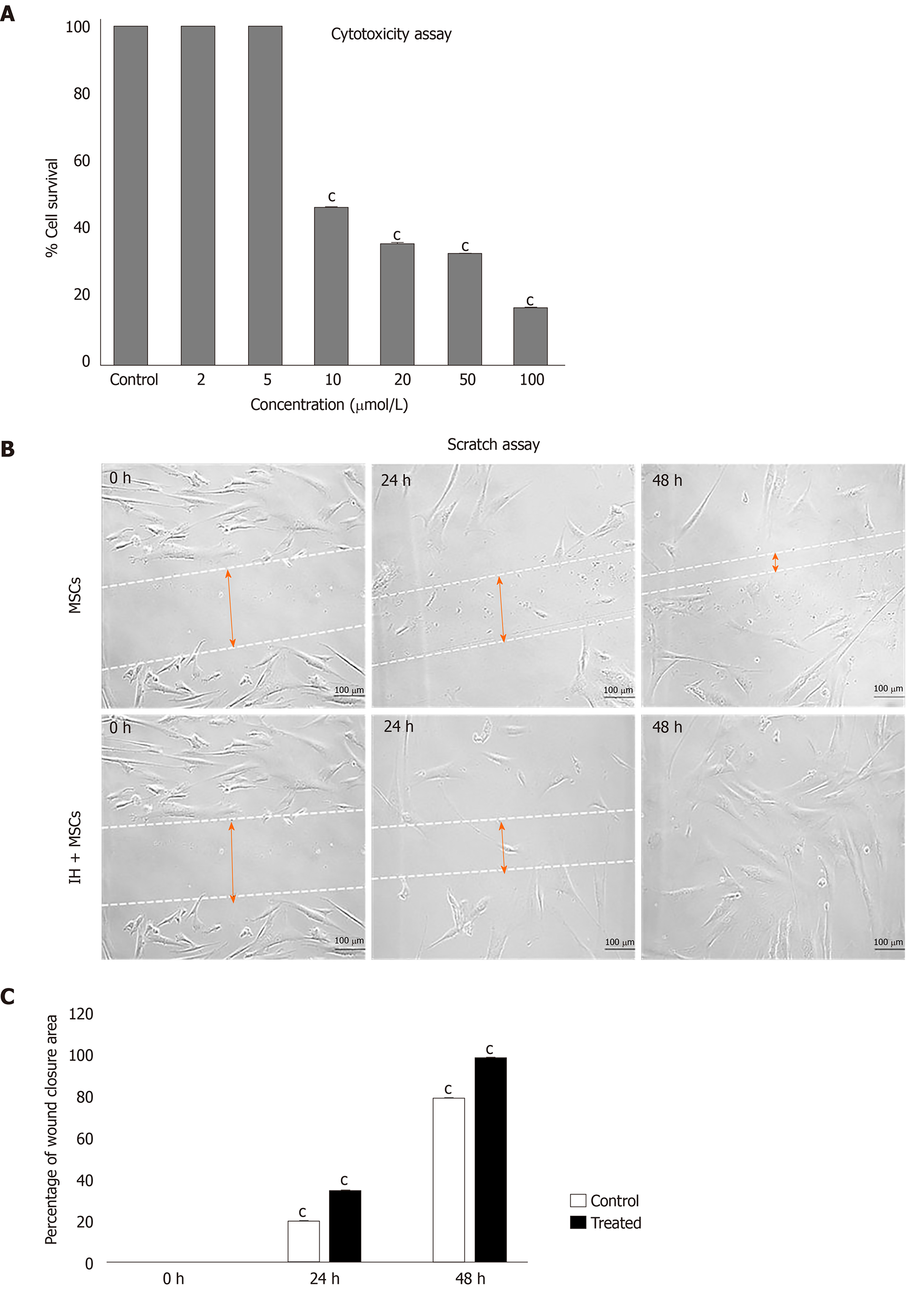
Figure 3 Cytotoxicity analysis and scratch assay.
A: MTT assay for cytotoxicity analysis showed a concentration dependent decrease in the viability of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) treated with isorhamnetin, with a significant reduction in the percentage of cell survival at concentrations above 5 µmol/L; B: Scratch assay shows cell migration of normal untreated MSCs and preconditioned MSCs (IH + MSCs) at 0, 24 and 48 h. The scratch area was reduced in IH + MSCs as compared to untreated MSCs after 24 h and complete migration was observed after 48 h. The quantitative analysis showed significant cell migration of isorhamnetin treated MSCs at 24 h and complete migration at 48 h as compared to untreated normal MSCs. For statistical analysis, One way ANOVA was performed, followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test; Data are presented as the mean ± SE (n = 4). cP < 0.001. MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; IH + MSCs: Preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells.
- Citation: Aslam S, Khan I, Jameel F, Zaidi MB, Salim A. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells preconditioned with isorhamnetin: potential therapy for burn wounds. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(12): 1652-1666
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i12/1652.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1652