Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2020; 12(12): 1623-1639
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1623
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1623
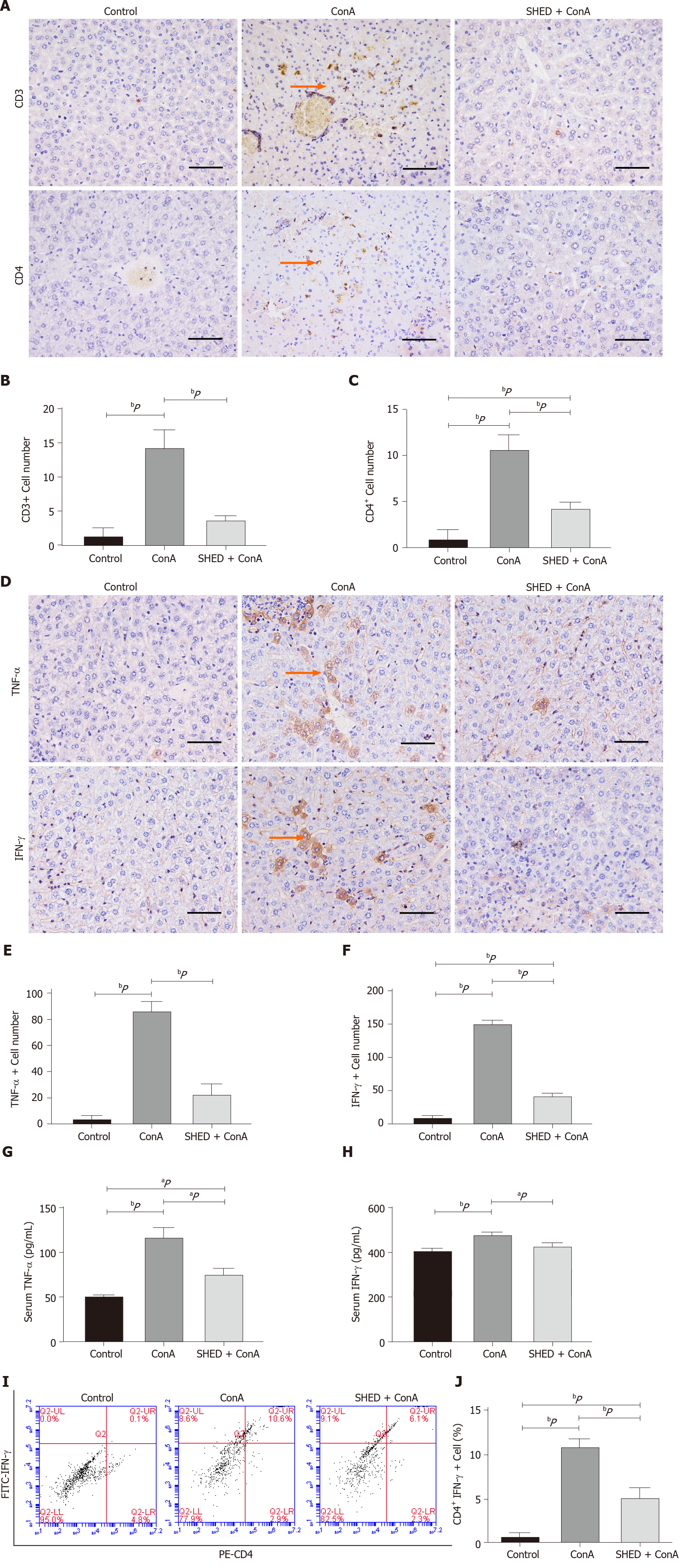
Figure 2 Pretreatment with stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth reduces inflammation in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis.
A: CD3+ and CD4+ T cell expression in liver tissues; B: Quantitative analysis of the number of CD3+ T cells; C: Quantitative analysis of the number of CD4+ T cells; D: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) expression in liver tissues; E: Quantitative analysis of the number of TNF-α+ cells; F: Quantitative analysis of the number of IFN-γ+ cells; G: Serum TNF-α levels; H: Serum IFN-γ levels. Arrows indicate positive cells in the liver section; I: Th1 cells detected by flow cytometry; J: Quantitative analysis of the percentage of CD4+ IFN-γ+ T cells; Scale bars = 100 μm. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; n ≥ 3.
- Citation: Zhou YK, Zhu LS, Huang HM, Cui SJ, Zhang T, Zhou YH, Yang RL. Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorate concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis by protecting hepatocytes from apoptosis. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(12): 1623-1639
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i12/1623.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1623