Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2020; 12(12): 1439-1454
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1439
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1439
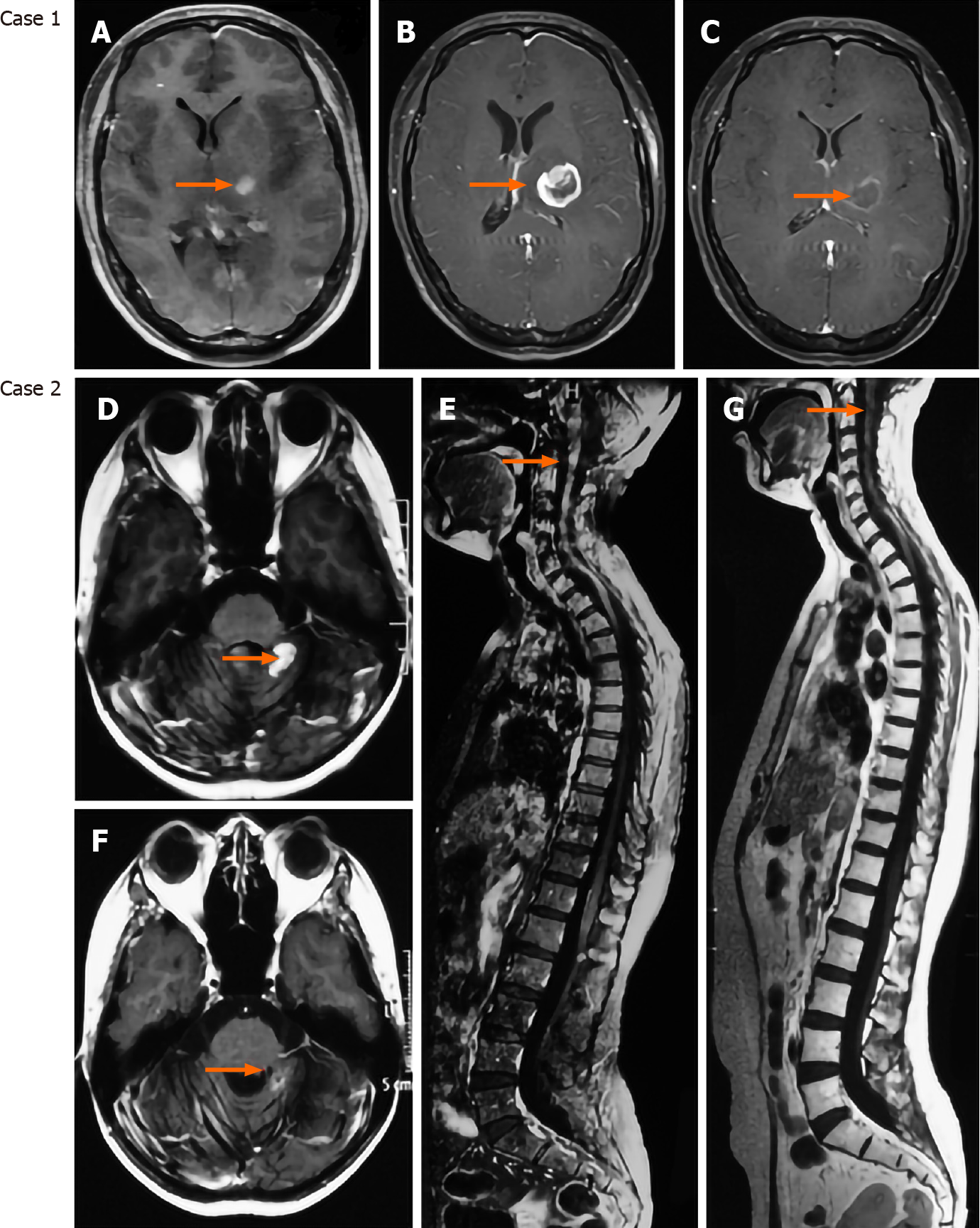
Figure 3 Targeting the vasculature presents promising effects on brain tumor therapy.
Case 1 is a 29-year-old female patient who was diagnosed with IDH1/2 wild-type glioblastoma and received treatment of temozolomide combined with apatinib. Case 2 is a 31-year-old female patient who was diagnosed with recurrent medulloblastoma (local recurrence and dissemination) and received temozolomide + irinotecan + bevacizumab. A: Axial enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showing a mass located at the left thalamus; B: Axial enhanced MRI showing that the lesion significantly progressed after 1-mo treatment of temozolomide; C: Axial enhanced MRI showing that the lesion was dramatically reduced after 1-mo treatment of combination of temozolomide and apatinib; D and E: Enhanced cerebrospinal MRI showing the local recurrent medulloblastoma and disseminated lesions along the spinal cord; F and G: Enhanced cerebrospinal MRI showing that the recurrent and disseminated lesions were significantly reduced after one cycle of chemotherapy.
- Citation: Liu HL, Wang YN, Feng SY. Brain tumors: Cancer stem-like cells interact with tumor microenvironment. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(12): 1439-1454
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i12/1439.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1439