Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2020; 12(11): 1410-1428
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i11.1410
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i11.1410
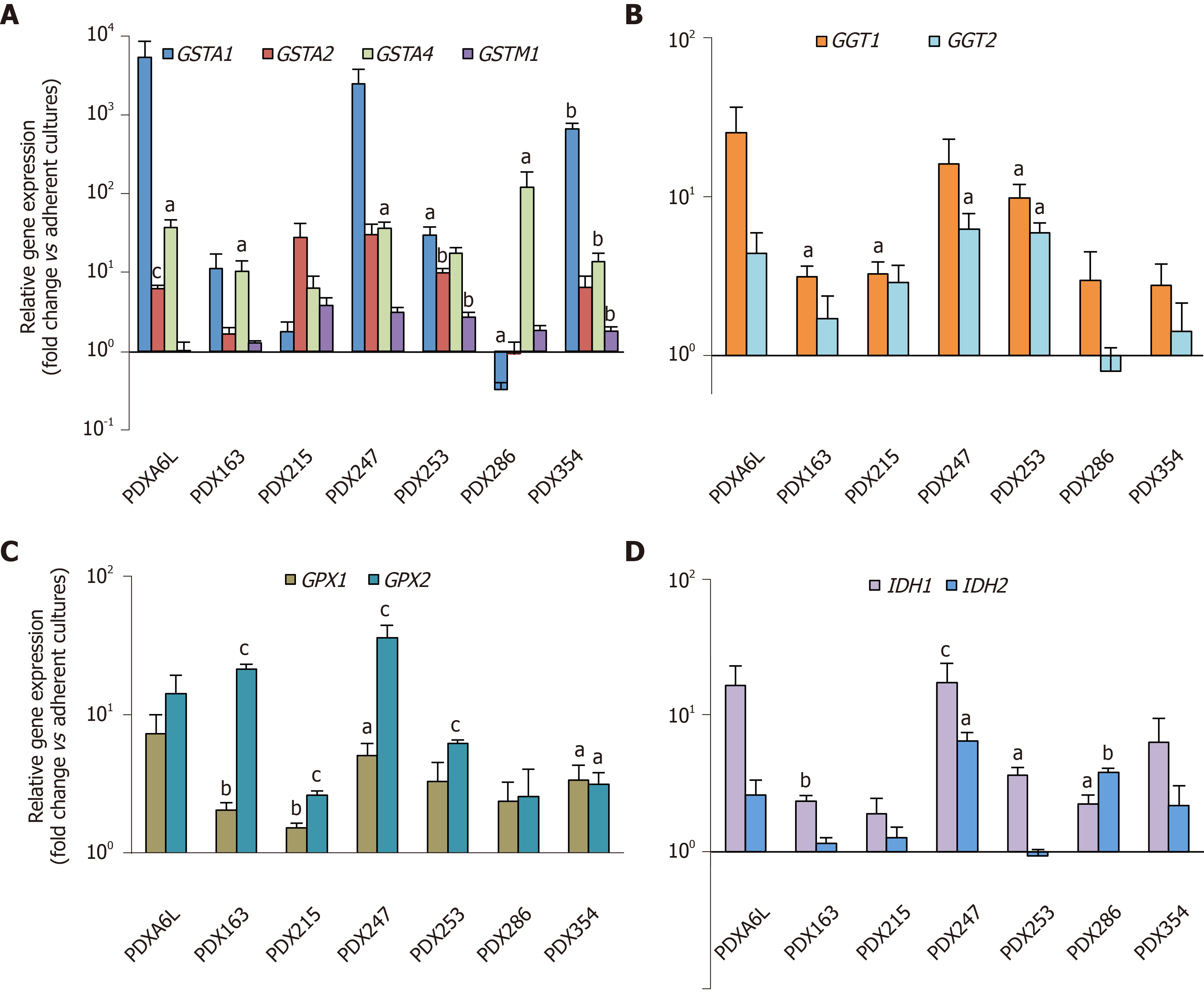
Figure 2 Glutathione metabolism-related genes are up-regulated in cancer stem cell-enriched conditions.
Primary cells from different patient-derived xenograft models as indicated in the figure were cultured in adherent or low-attachment cancer stem cell-enriching conditions. On day 7 the expression of several glutathione (GSH)-related genes was evaluated by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A: Glutathione-S-Transferases A1, A2, A4, M1; B: Gamma-glutamyltransferases 1 and 2; C: Glutathione Peroxidases 1 and 2; D: Isocitrate Dehydrogenases 1 and 2. Data were normalized to HPRT and are shown as mean ± SE fold change expression levels of sphere vs adherent cultures in logarithmic scale. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. PDX: Patient-derived xenograft; GGT: Gamma-glutamyltransferase; GST: Glutathione-s-transferase; GPX: Glutathione peroxidase.
- Citation: Jagust P, Alcalá S, Sainz Jr B, Heeschen C, Sancho P. Glutathione metabolism is essential for self-renewal and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(11): 1410-1428
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i11/1410.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i11.1410