Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2020; 12(11): 1237-1254
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i11.1237
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i11.1237
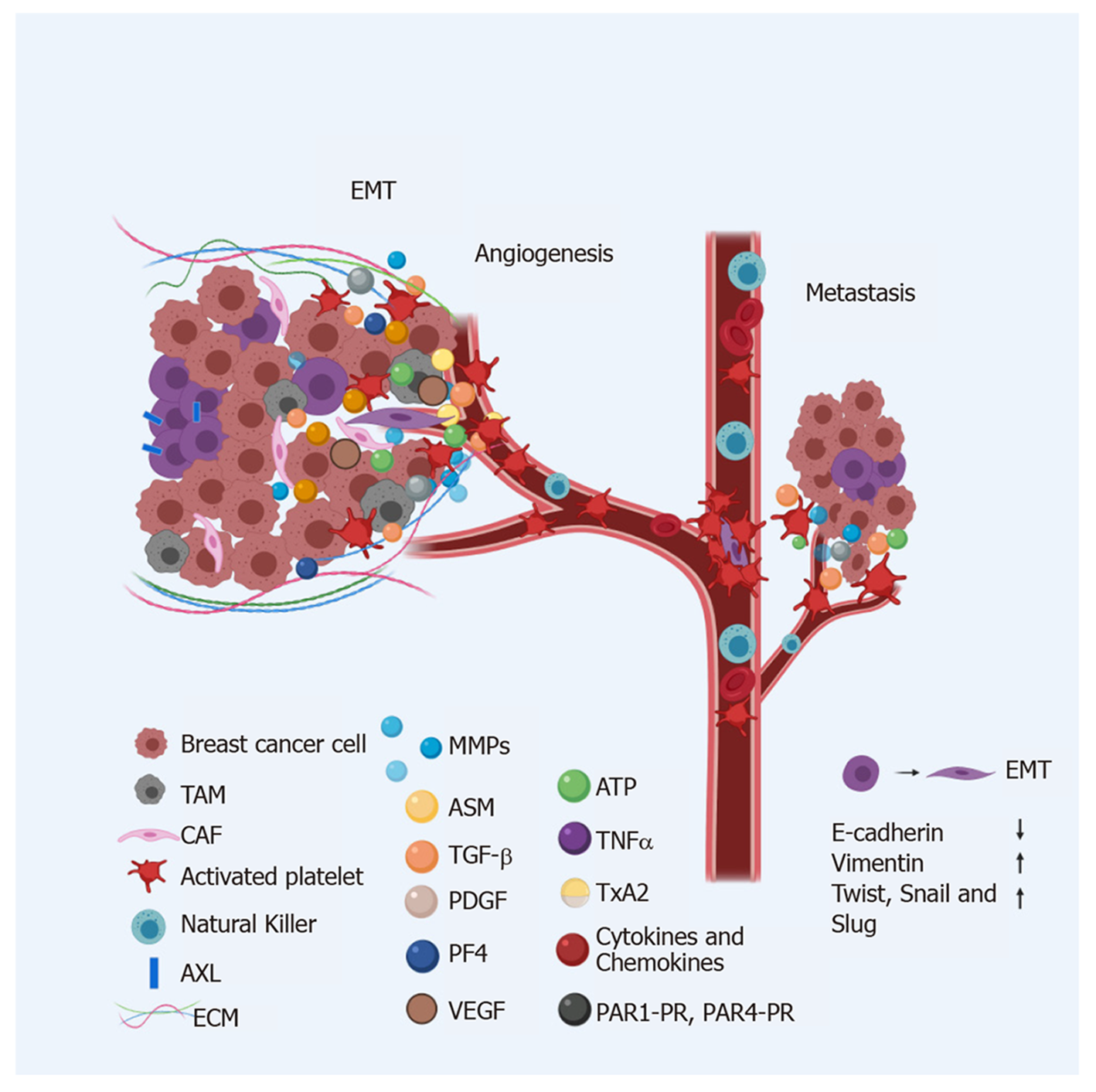
Figure 3 Breast cancer metastasis.
Metastatic foci are the product of a series of events and in all these steps, they are accompanied by platelets. Breast cancer stem cell (BCSC) receives stimuli from the tumor microenvironment, including platelets, to allow the cellular transition epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Once the BCSC has achieved cell transformation and has broken the intercellular junctions and the extracellular matrix, it passes through the bloodstream or lymphatic system, always accompanied by platelets to avoid anoikis, shear forces and natural killer cells. The tumor educated platelets prepare the second metastatic niche. Created by Biorender.com. EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophage; CAF: Cancer-associated fibroblast; ECM: Extracellular matrix. Created with Biorender.com
- Citation: Mendoza-Almanza G, Burciaga-Hernández L, Maldonado V, Melendez-Zajgla J, Olmos J. Role of platelets and breast cancer stem cells in metastasis. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(11): 1237-1254
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i11/1237.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i11.1237