Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2020; 12(10): 1196-1213
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1196
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1196
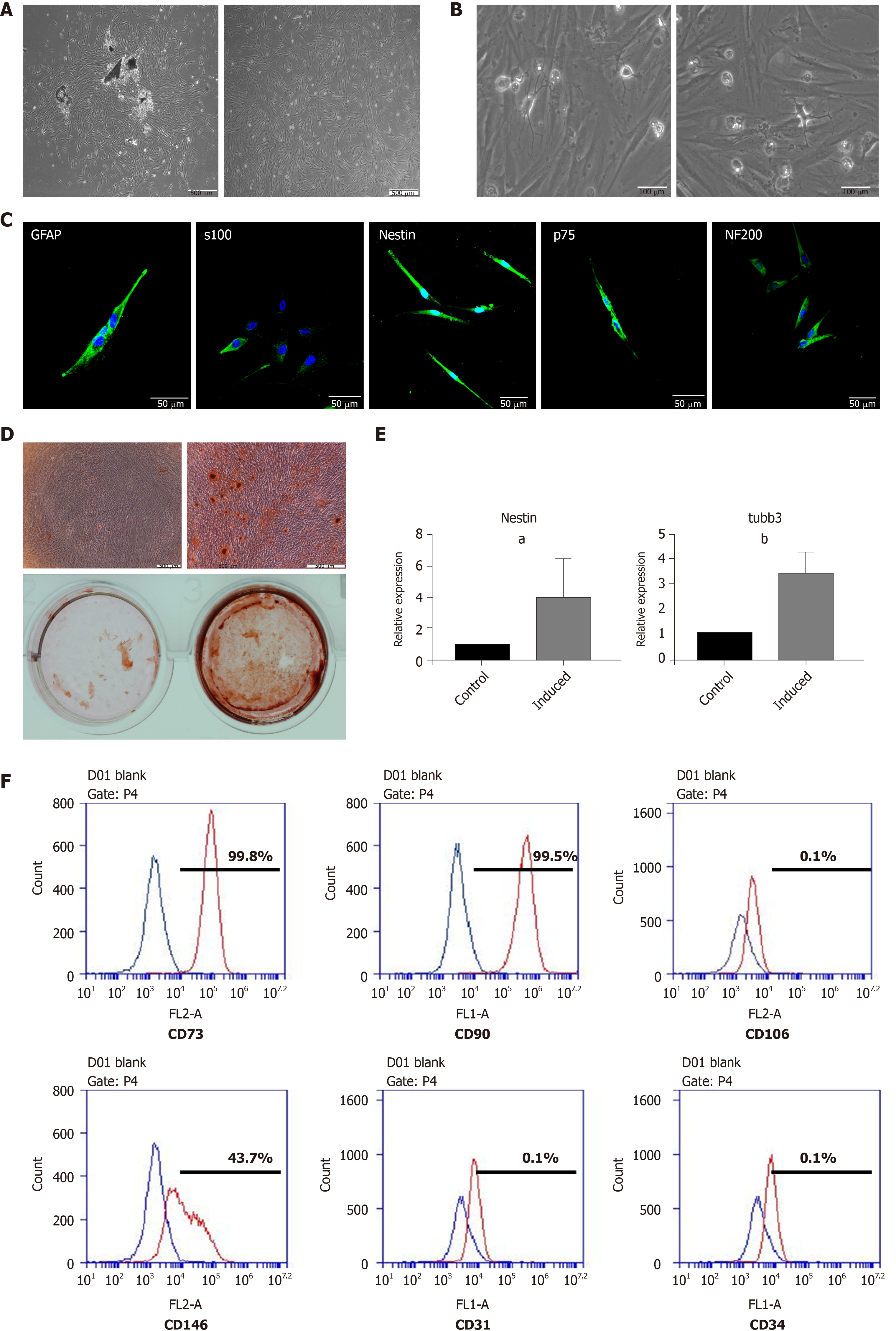
Figure 1 Isolation, culture, and multilineage differentiation of dental pulp stem cells.
A: Morphology of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs); B: Neural-like cells differentiated from DPSCs; C: Immunofluorescent staining for Nestin, S100, GFAP, p75, and NF200; D: Osteogenic induction; E: Neural induction assessed by real-time PCR; F: Flow cytometry for CD73, CD90, CD146, CD106, CD31, and CD34. Student’s t test was used to identify statistical significance. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Wang DR, Wang YH, Pan J, Tian WD. Neurotrophic effects of dental pulp stem cells in repair of peripheral nerve after crush injury. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(10): 1196-1213
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i10/1196.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1196