Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2020; 12(10): 1184-1195
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1184
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1184
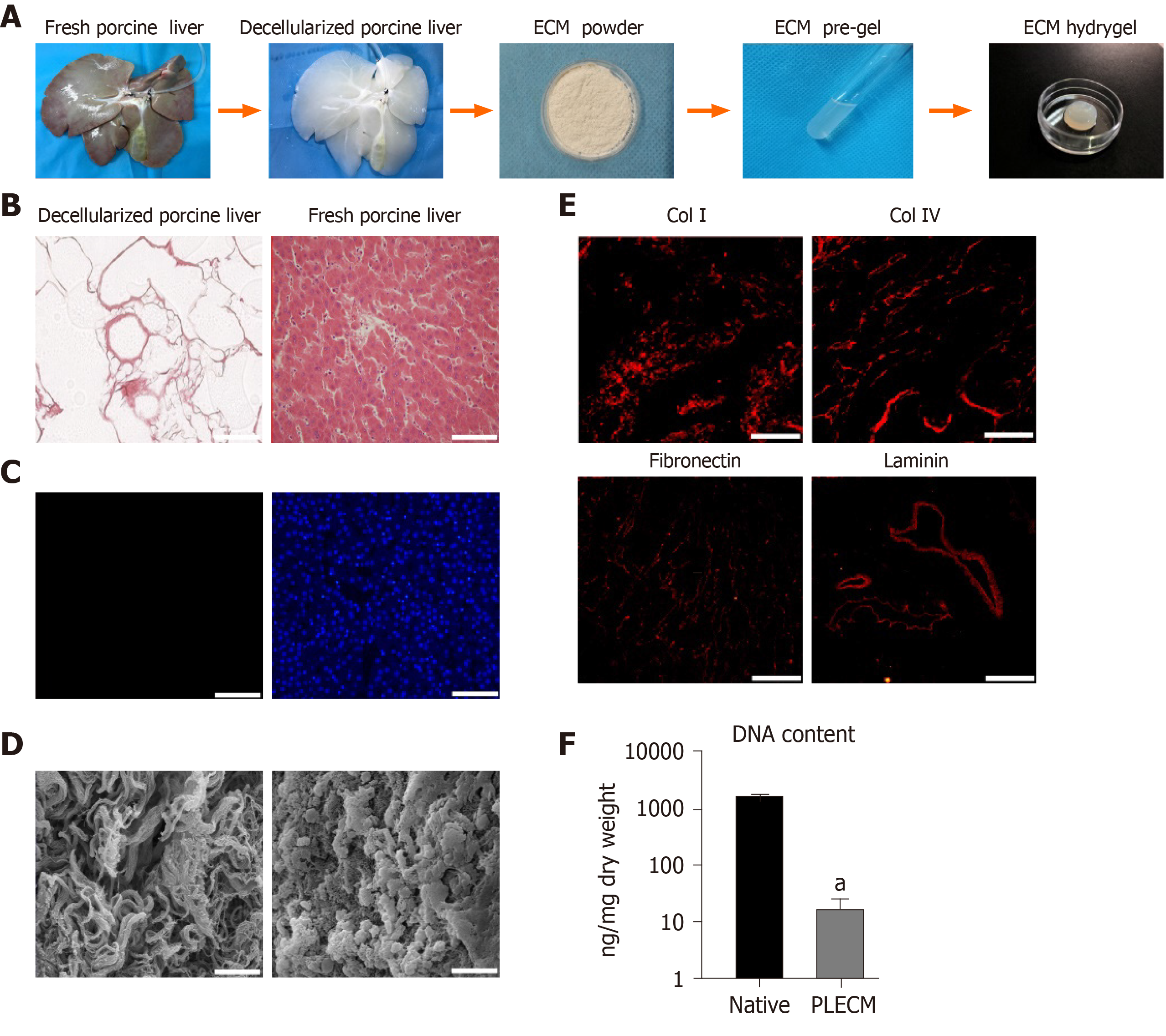
Figure 1 Formation and characterization of porcine liver extracellular matrix gel.
A: Procedure for the formation of porcine liver extracellular matrix (PLECM) gels; B: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining of PLECM (left) and porcine liver (right). Scale bars = 100 μm; C: 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole staining of PLECM (left) and porcine liver (right). Scale bars = 100 μm; D: Scanning electron microscopy of PLECM (left) and porcine liver (right). Scale bars = 20 μm; E: Immunohistochemistry (red) for liver extracellular matrix proteins (collagen type I, collagen type IV, fibronectin, and laminin) in PLECM. Scale bars = 200 μm; F: Relative DNA content. aP < 0.05 vs PLECM. ECM: Extracellular matrix; Col I: Collagen type I; Col IV: Collagen type IV; PLECM: Porcine liver extracellular matrix.
- Citation: He YT, Zhu XL, Li SF, Zhang BQ, Li Y, Wu Q, Zhang YL, Zhou YY, Li L, Qi YN, Bao J, Bu H. Creating rat hepatocyte organoid as an in vitro model for drug testing. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(10): 1184-1195
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i10/1184.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1184