Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2020; 12(10): 1133-1151
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1133
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1133
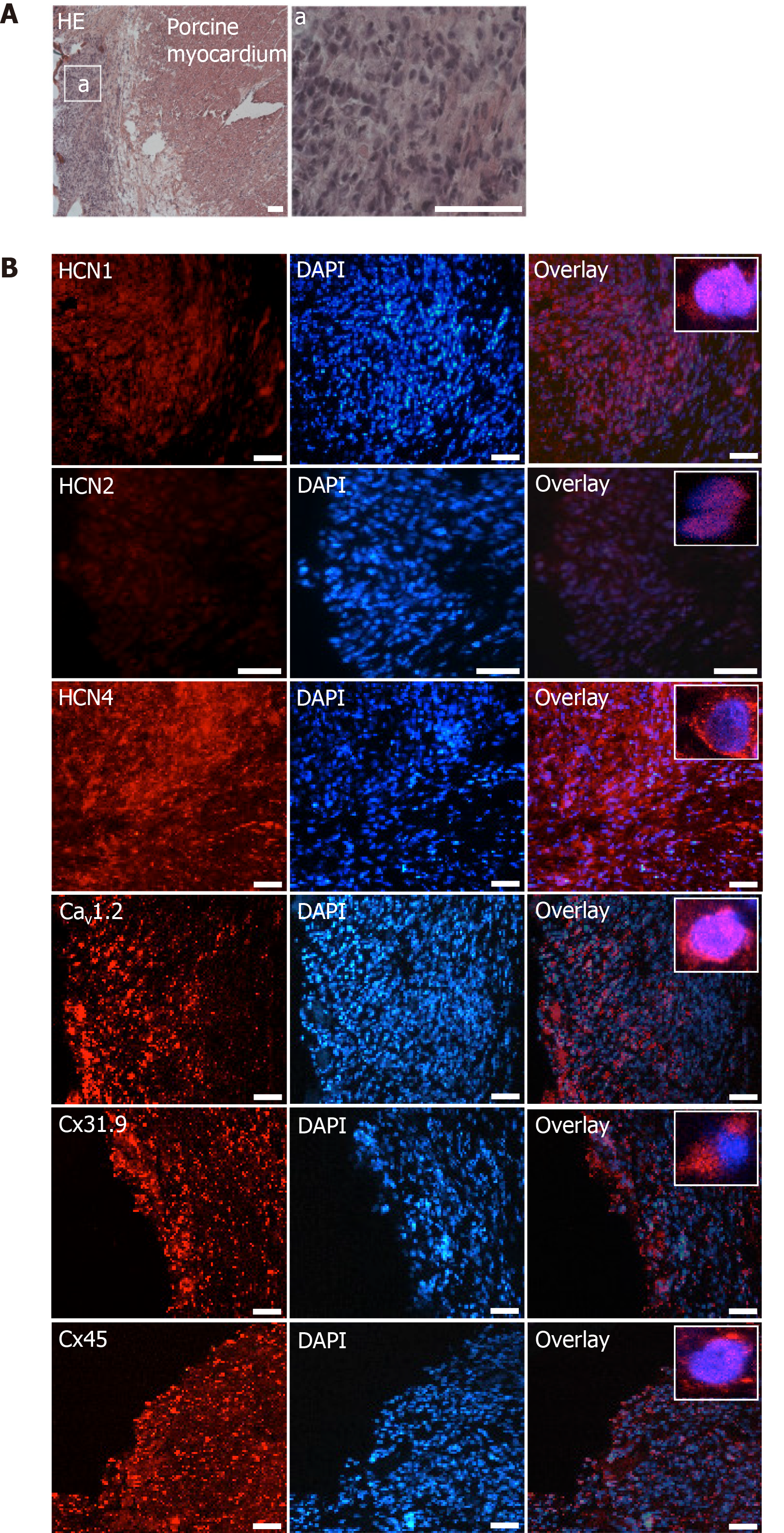
Figure 8 Microscopic analysis of transplanted differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue within porcine myocardium.
A: HE staining of cryosections showing the engraftment of injected differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue (dhaMSC) into porcine myocardium. Overview and dhaMSC area (a); B left: Immunohistochemistry of HCN1, HCN2, HCN4, Cav1.2, Cx31.9 and Cx45. B middle: Nuclei counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). B: Right, overlay of immunohistochemistry and DAPI counterstain. Scale bars: 50 nm. DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
- Citation: Darche FF, Rivinius R, Rahm AK, Köllensperger E, Leimer U, Germann G, Reiss M, Koenen M, Katus HA, Thomas D, Schweizer PA. In vivo cardiac pacemaker function of differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue transplanted into porcine hearts. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(10): 1133-1151
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i10/1133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1133