Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2020; 12(10): 1133-1151
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1133
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1133
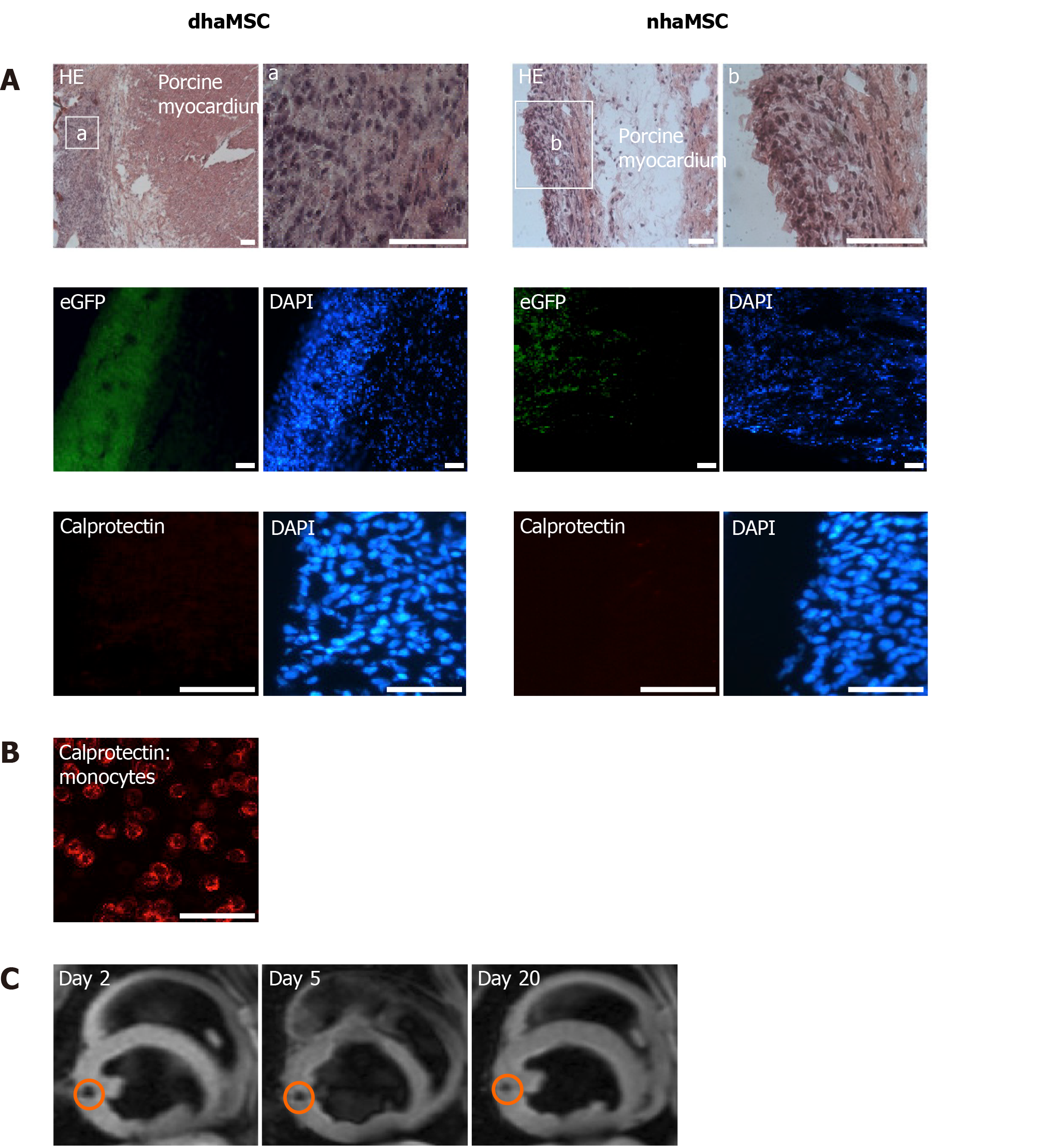
Figure 7 Localization and immunogenicity of xenotransplanted differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue and native human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue in the left ventricle of porcine myocardium.
A: Localization of enhanced green fluorescent protein-transfected differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue (dhaMSC) and native human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue (nhaMSC) within porcine myocardium. dhaMSC and nhaMSC are negative for calprotectin, a marker of immune reaction; B: Control test with monocytes, which are positive for calprotectin. Scale bars: 50 nm; C: Magnetic resonance imaging of superparamagnetic iron oxides-labeled dhaMSC (orange circle) transplanted into porcine myocardium, performed on days 2, 5 and 20 after cell injection. dhaMSC: Differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue; nhaMSC: Native human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue; eGFP: Enhanced green fluorescent protein; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
- Citation: Darche FF, Rivinius R, Rahm AK, Köllensperger E, Leimer U, Germann G, Reiss M, Koenen M, Katus HA, Thomas D, Schweizer PA. In vivo cardiac pacemaker function of differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue transplanted into porcine hearts. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(10): 1133-1151
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i10/1133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1133