Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2020; 12(10): 1133-1151
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1133
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1133
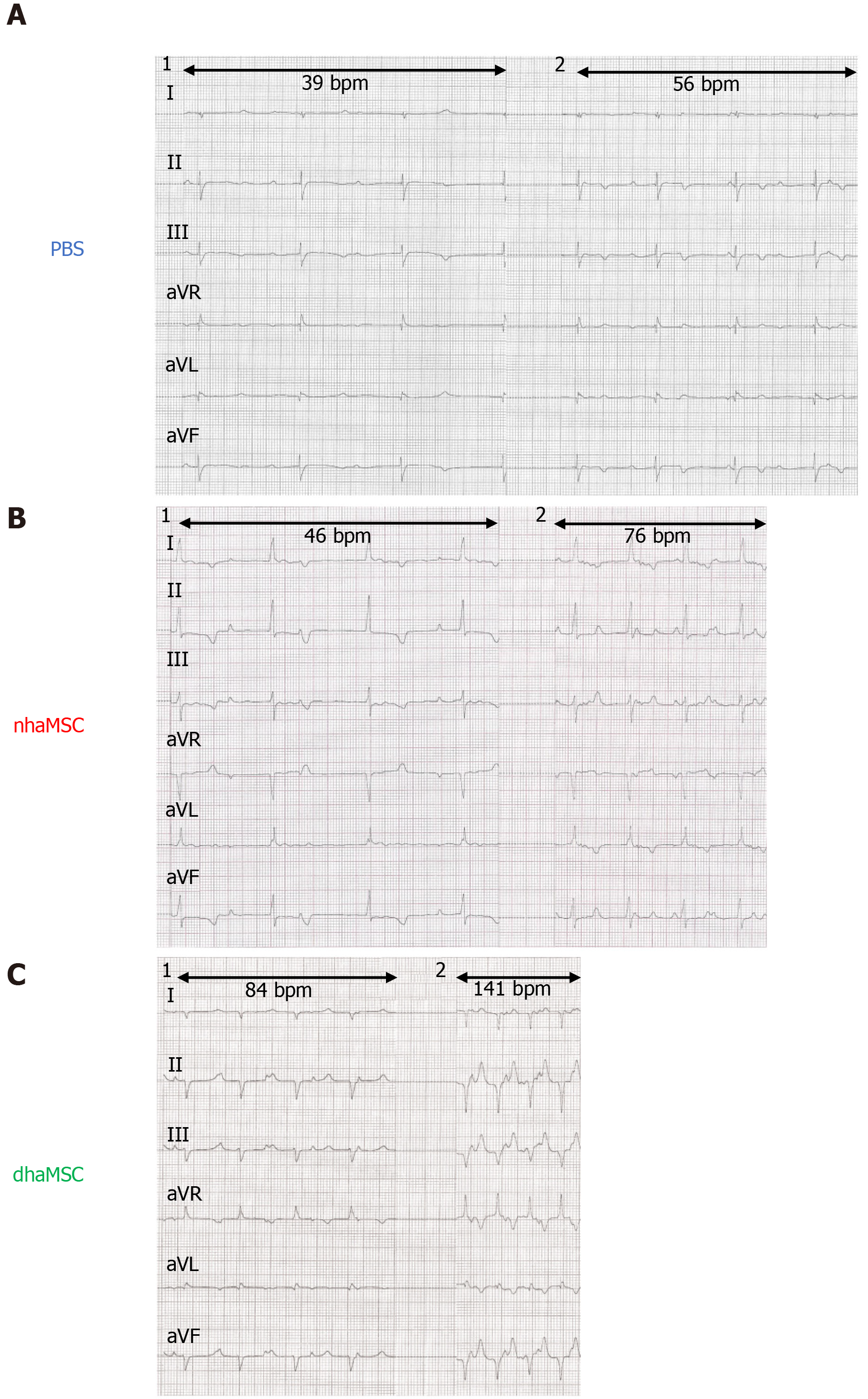
Figure 4 Electrocardiograms of ventricular escape rhythms after atrioventricular node ablation.
A: Phosphate-buffered saline group; B: Native human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue group; C: Differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue group. 1: Baseline ventricular escape rhythms. 2: Stimulated ventricular escape rhythm by epinephrine (1 mg) IV and atropine (0.5 mg) IV. Electrocardiograms recorded at a speed of 25 mm/s. PBS: Phosphate-buffered saline; nhaMSC: Native human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue; dhaMSC: Differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue.
- Citation: Darche FF, Rivinius R, Rahm AK, Köllensperger E, Leimer U, Germann G, Reiss M, Koenen M, Katus HA, Thomas D, Schweizer PA. In vivo cardiac pacemaker function of differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue transplanted into porcine hearts. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(10): 1133-1151
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i10/1133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1133