Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2020; 12(10): 1133-1151
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1133
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1133
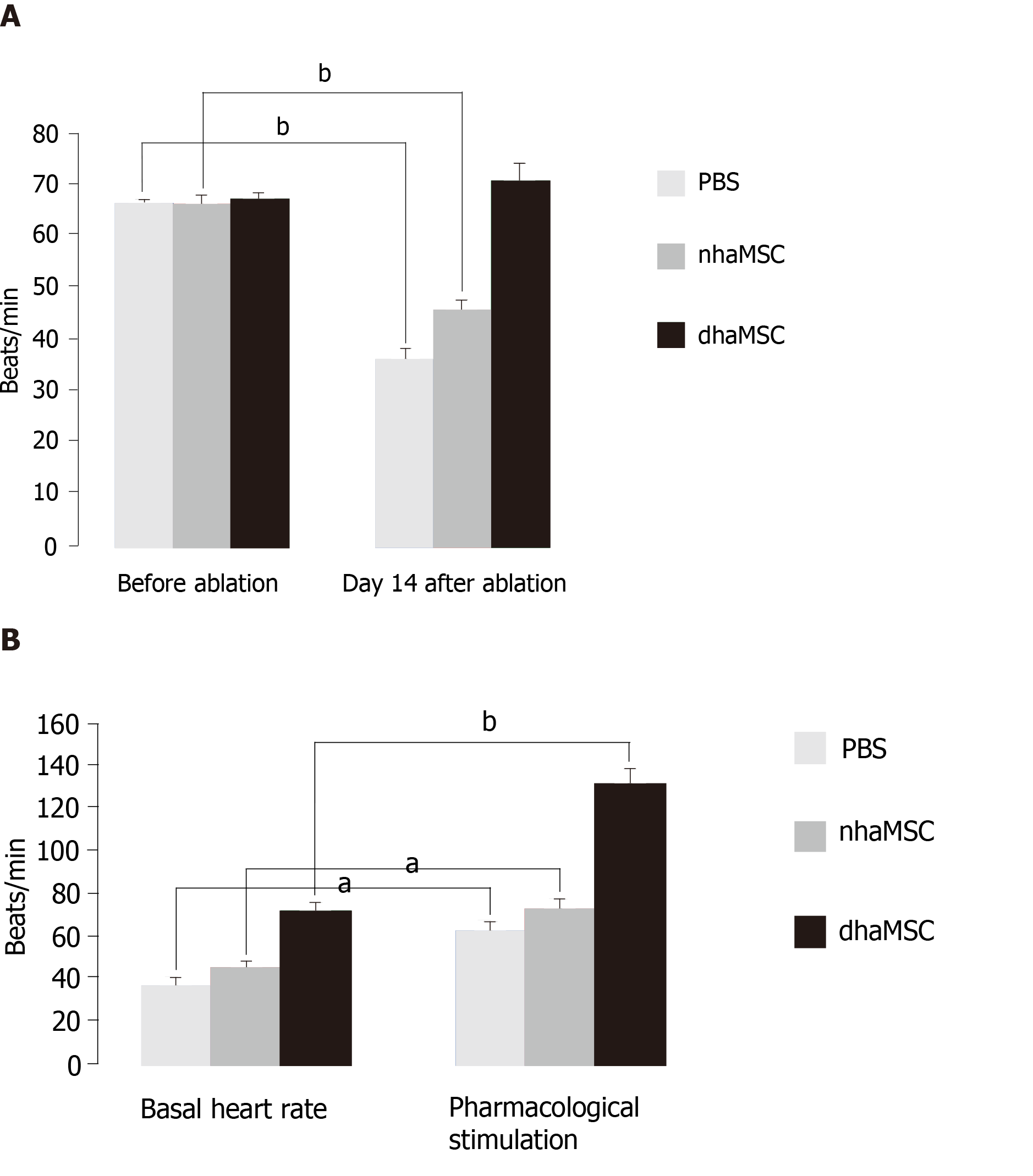
Figure 2 Heart rate assessment.
Evaluated by electrocardiogram (ECG) recordings in pigs with transplanted differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue (green, n = 6) or transplanted native human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue (red, n = 6) and in pigs treated with PBS (blue, n = 6). A: Intrinsic heart rate recordings before ablation and on day 14 after ablation (intervention rate of the electronic pacemaker device switched from 40 to 30 bpm during recordings); B: Basal and stimulated heart rates, recorded on day 14 after ablation. Chronotropic responsiveness was induced by simulation with epinephrine (1 mg) IV and atropine (0.5 mg) IV. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001, showing statistical significance. PBS: Phosphate-buffered saline; nhaMSC: Native human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue; dhaMSC: Differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue.
- Citation: Darche FF, Rivinius R, Rahm AK, Köllensperger E, Leimer U, Germann G, Reiss M, Koenen M, Katus HA, Thomas D, Schweizer PA. In vivo cardiac pacemaker function of differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue transplanted into porcine hearts. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(10): 1133-1151
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i10/1133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1133