Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2020; 12(1): 70-86
Published online Jan 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i1.70
Published online Jan 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i1.70
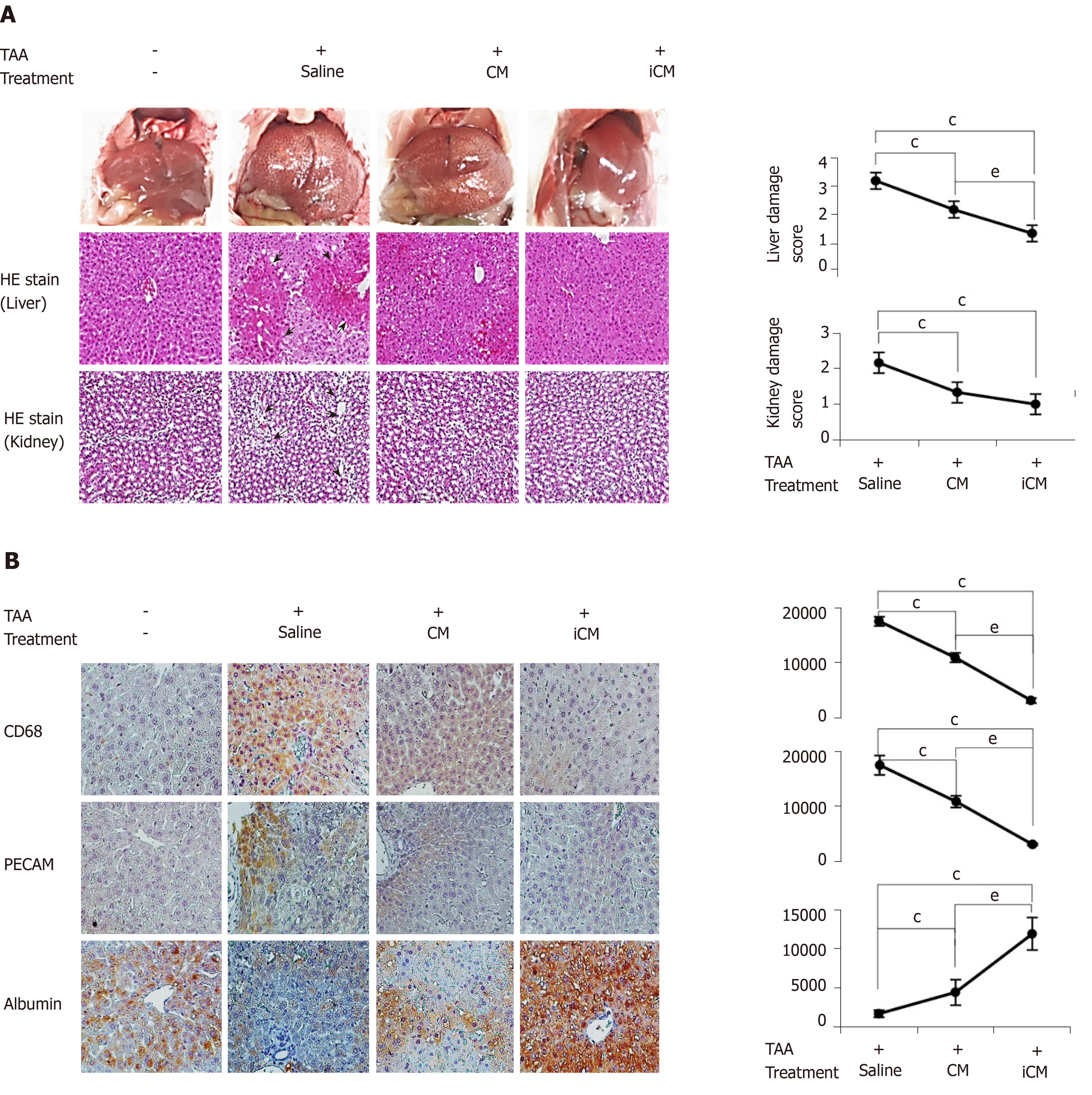
Figure 5 Various stains validating effects of thioacetamide-induced secretome in the mouse model of thioacetamide-induced hepatic failure.
A: TAA-induced conditioned media infusion significantly decreased both liver damage and kidney damage scores calculated based on hematoxylin and eosin staining; B: Immunohistochemical staining of liver specimens. Immunohistochemical stains showed that TAA-induced conditioned media infusion significantly decreased the expression of inflammatory markers (CD68 and PECAM) and significantly increased the expression of albumin. Values are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. cP < 0.05 vs control (saline); eP < 0.05 between conditioned media and induced conditioned media. iCM: Induced secretome group of which components were the TAA-induced secretome; CM: Normal conditioned media group of which components were the naïve secretome; TAA: Thioacetamide.
- Citation: Kim OH, Hong HE, Seo H, Kwak BJ, Choi HJ, Kim KH, Ahn J, Lee SC, Kim SJ. Generation of induced secretome from adipose-derived stem cells specialized for disease-specific treatment: An experimental mouse model. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(1): 70-86
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i1/70.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i1.70