Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2020; 12(1): 70-86
Published online Jan 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i1.70
Published online Jan 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i1.70
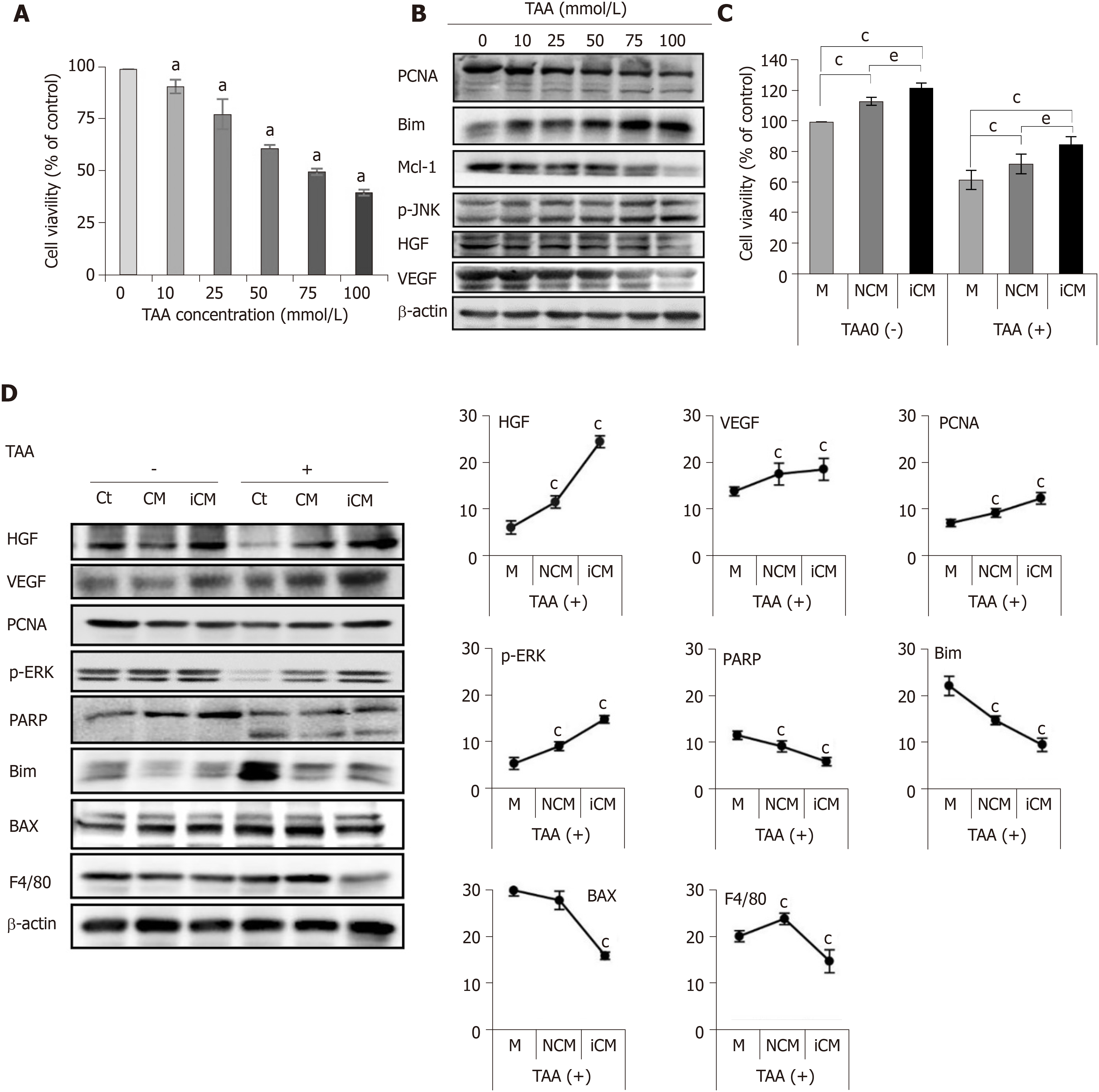
Figure 2 Determination of in vitro effects of thioacetamide-induced secretome.
A, B: Cell proliferation test (A) and western blotting (B) of AML12 cells to determine TAA concentration for generating an in vitro model of TAA-induced hepatic failure. A TAA concentration of 50 mM was used for TAA-induced hepatocytes; C, D: Effects of the TAA-induced secretome on the in vitro model of TAA-induced hepatic failure. Cell proliferation test (C) demonstrated that induced conditioned media-treated hepatocytes showed the highest cell proliferation in both normal and TAA-treated hepatocytes. In western blot analysis (D), induced conditioned media-treated hepatocytes showed the highest expression of liver regeneration markers and lowest expression of apoptosis and inflammation markers. Values are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05; cP < 0.05 vs media; eP < 0.05 between conditioned media and induced conditioned media. Bax: Bcl-2-like protein 4; BIM: Bcl-2-like protein 11; Ct: Control; iCM: Induced secretome group of which components were the TAA-induced secretome; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; M: Media group of which components were commercialized conditioned media; Mcl-1: Myeloid cell leukemia 1; CM: Normal conditioned media group of which components were the naïve secretome; PARP: Poly adenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; p-ERK: Phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinases; p-JNK: Phosphorylated Jun N-terminal kinase; TAA: Thioacetamide; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Kim OH, Hong HE, Seo H, Kwak BJ, Choi HJ, Kim KH, Ahn J, Lee SC, Kim SJ. Generation of induced secretome from adipose-derived stem cells specialized for disease-specific treatment: An experimental mouse model. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(1): 70-86
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i1/70.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i1.70