Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2019; 11(9): 705-721
Published online Sep 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i9.705
Published online Sep 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i9.705
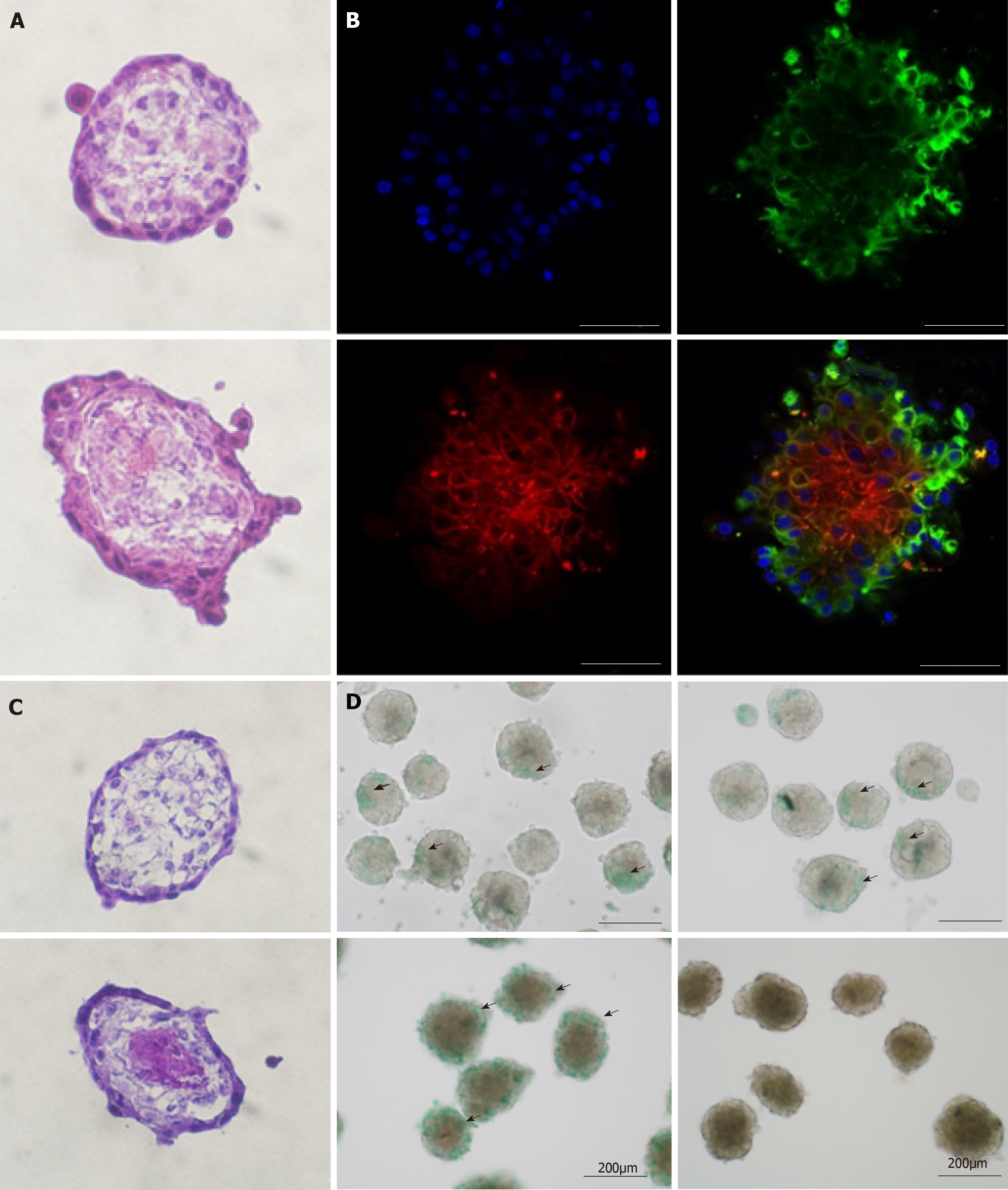
Figure 4 Organoid morphology and hepatic function.
A and C: Frozen sections of amniotic epithelial cell (AEC) sphere and organoid. The AEC sphere was placed in the upper layer and the organoid was placed in the lower layer. H&E staining is used in A, and Periodic acid Schiff staining is used in C; B: Immunofluorescent organoid staining observed under confocal microscopy. Anti-SSEA4 antibody (green) representing AECs; anti-CD90 antibody (red) representing mesenchymal stem cells and DAPI. Bars in A, B, and C, 50 µm; D: ICG tests on AEC sphere and organoid. The AEC sphere was placed in the upper layer and the organoid was placed in the lower layer.
- Citation: Furuya K, Zheng YW, Sako D, Iwasaki K, Zheng DX, Ge JY, Liu LP, Furuta T, Akimoto K, Yagi H, Hamada H, Isoda H, Oda T, Ohkohchi N. Enhanced hepatic differentiation in the subpopulation of human amniotic stem cells under 3D multicellular microenvironment. World J Stem Cells 2019; 11(9): 705-721
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v11/i9/705.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i9.705