Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2019; 11(9): 705-721
Published online Sep 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i9.705
Published online Sep 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i9.705
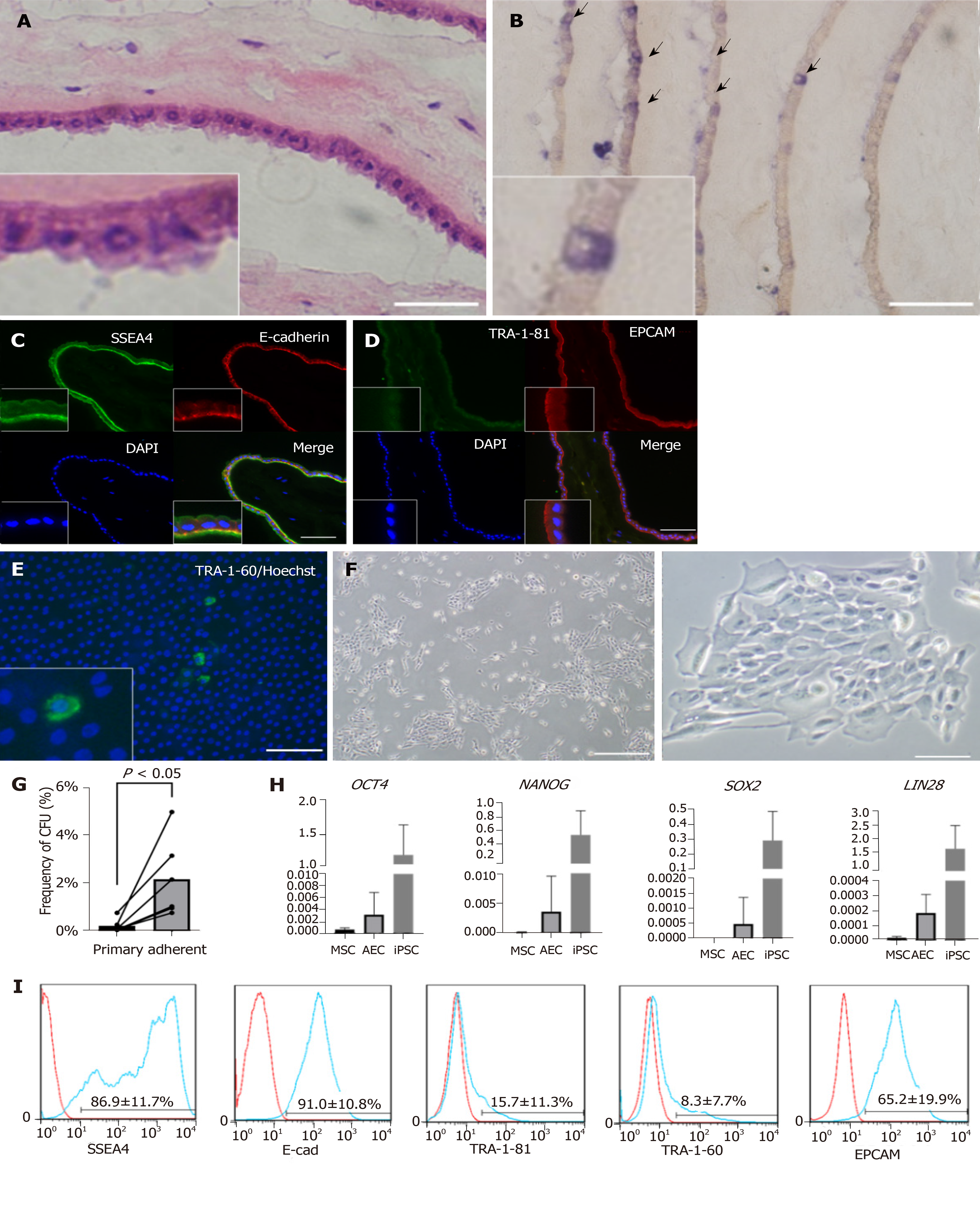
Figure 1 Characteristics of human amniotic membrane and amniotic epithelial cells.
A: H and E staining of amniotic membrane. Bar, 50 µm; B: AP staining of amniotic membrane. Positive cells are indicated with arrows. Bar, 100 µm. In A and B, the amniotic membrane was rolled before embedding. Therefore, many layers can be seen in one picture; C: Immunofluorescent staining of frozen section of amniotic membrane. Anti-SSEA4 antibody (green), E-cadherin antibody (red), and DAPI were used; D: Same as C. Anti-TRA-1-81 antibody (green), anti-EPCAM antibody (red), and DAPI were used; E: Direct tissue staining of amniotic membrane. Anti-TRA-1-60 antibody (green) and DAPI were used. Bars in C, D, and E represent 100 µm; F: Colonies formed from cultured amniotic epithelial cells (AECs) and observed by phase-contrast microscopy. Bar to left of F represents 200 µm. Bar to right of F represents 500 µm; G: Frequency of colony formation from primary AECs and adherent AECs. Cells which did not attach to the well surface were removed to purify the amniotic stem cells; H: Gene expression of primary AECs, mesenchymal stem cells(MSCs), and induced pluripotent stem cells(iPSCs) detected by qRT-PCR; I: surface markers of primary AECs verified by flow cytometry.
- Citation: Furuya K, Zheng YW, Sako D, Iwasaki K, Zheng DX, Ge JY, Liu LP, Furuta T, Akimoto K, Yagi H, Hamada H, Isoda H, Oda T, Ohkohchi N. Enhanced hepatic differentiation in the subpopulation of human amniotic stem cells under 3D multicellular microenvironment. World J Stem Cells 2019; 11(9): 705-721
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v11/i9/705.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i9.705