Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2019; 11(9): 650-665
Published online Sep 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i9.650
Published online Sep 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i9.650
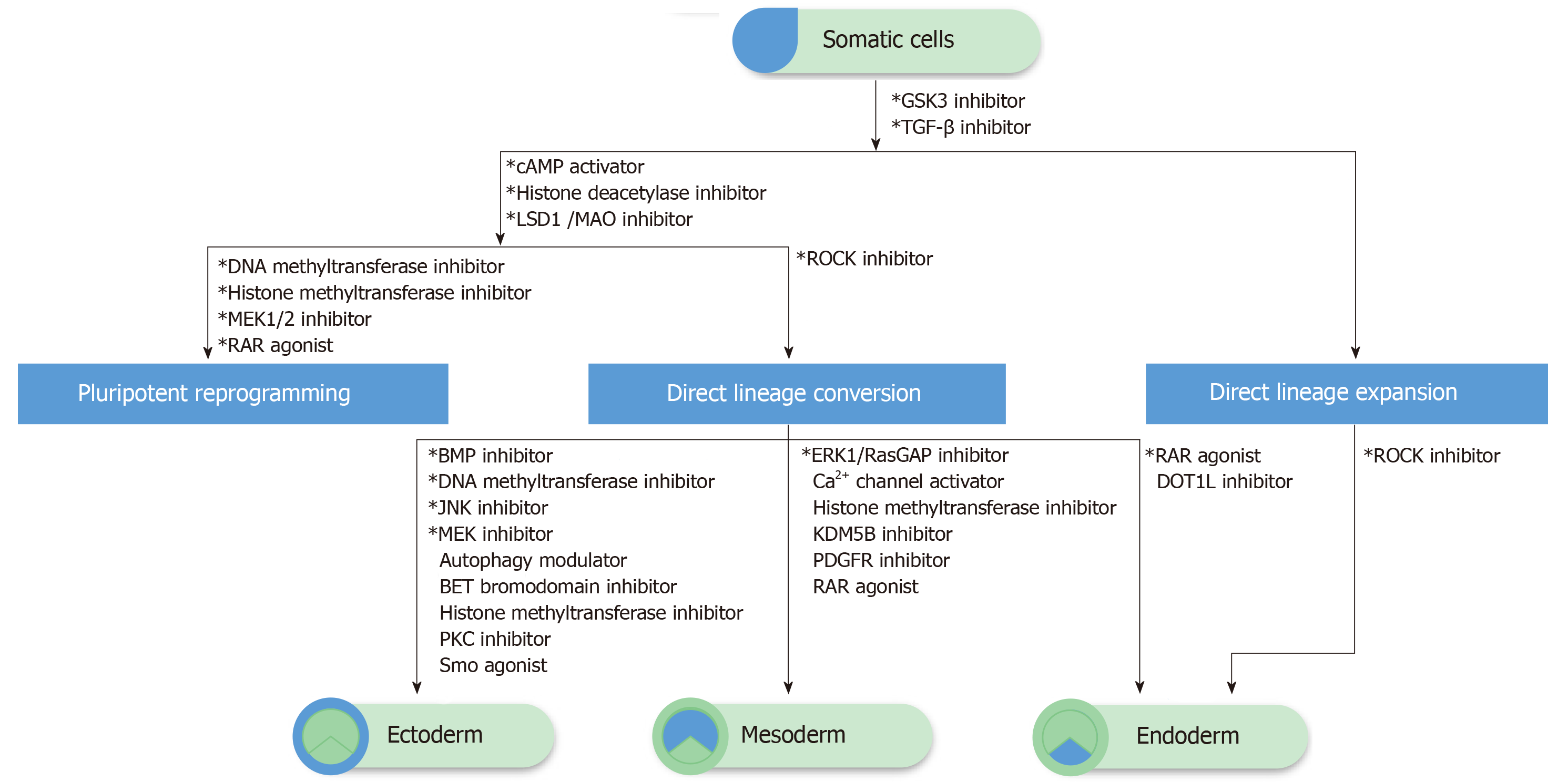
Figure 1 The schematic of chemical-driven cell fate change and expansion.
The transforming growth factor (TGF)-β and GSK3 pathway inhibitors are commonly required in pluripotency reprogramming, direct lineage conversion, and expansion. Additional epigenetic modulators (histone deacetylase inhibitors and/or deoxyribonucleic acid/histone methyltransferase inhibitors) are applied for pluripotency reprogramming, as well as direct lineage conversion, while different lineage commitments require specific signaling modulations. The combination of TGF-β, GSK3, and ROCK pathway inhibitors could induce the direct lineage expansion of endoderm-committed cells such as hepatocytes. The direct expansion of ectoderm and mesoderm-committed cells remains unclear and could not be listed here. *Necessary and/or commonly used compounds.
- Citation: Ge JY, Zheng YW, Liu LP, Isoda H, Oda T. Impelling force and current challenges by chemicals in somatic cell reprogramming and expansion beyond hepatocytes. World J Stem Cells 2019; 11(9): 650-665
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v11/i9/650.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i9.650