Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2019; 11(9): 618-633
Published online Sep 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i9.618
Published online Sep 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i9.618
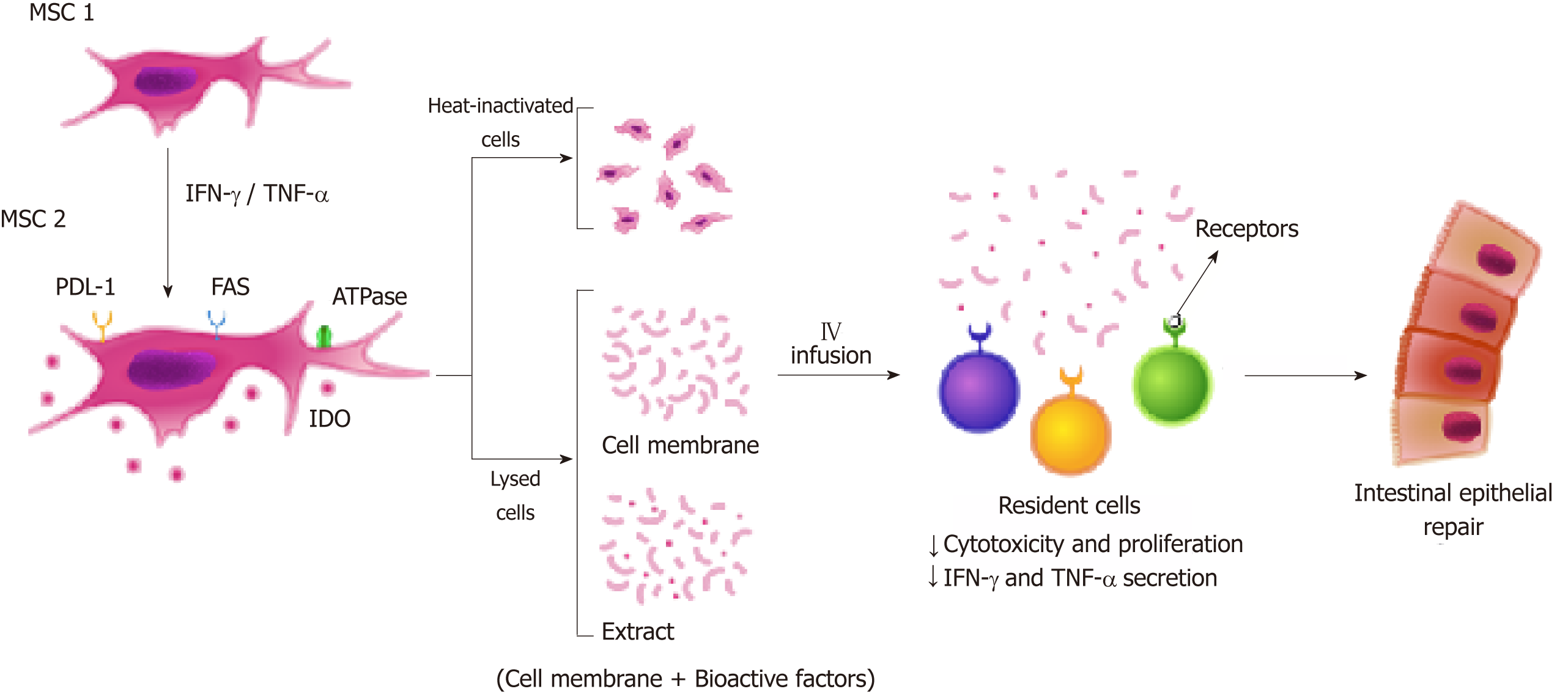
Figure 2 Enhanced immunosuppressive properties of MSC in cell contact-dependent mechanism.
Treatment with IFN-γ and TNF-α induce MSC1 to express immunomodulatory molecules (MSC2) that mediate the suppression via cell contact-dependent mechanisms including PD-L1/PD-1 pathway and FAS-L/FAS interaction. To improve MSC homing, new therapeutic approaches are being developed: Heat-inactivated cells and lysed cells (extract or cell membrane). MSC-based therapy may exert its therapeutic effects mainly by cell-cell contact and consequently by interaction with immune cells, establishing a favorable environment for the regeneration of intestinal tissue. MSC: Mesenchymal stromal cells; IFN: Interferon; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; PD-L1: Programmed death ligand 1; IDO: Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase.
- Citation: da Costa Gonçalves F, Paz AH. Cell membrane and bioactive factors derived from mesenchymal stromal cells: Cell-free based therapy for inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Stem Cells 2019; 11(9): 618-633
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v11/i9/618.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i9.618