Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2019; 11(8): 452-463
Published online Aug 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i8.452
Published online Aug 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i8.452
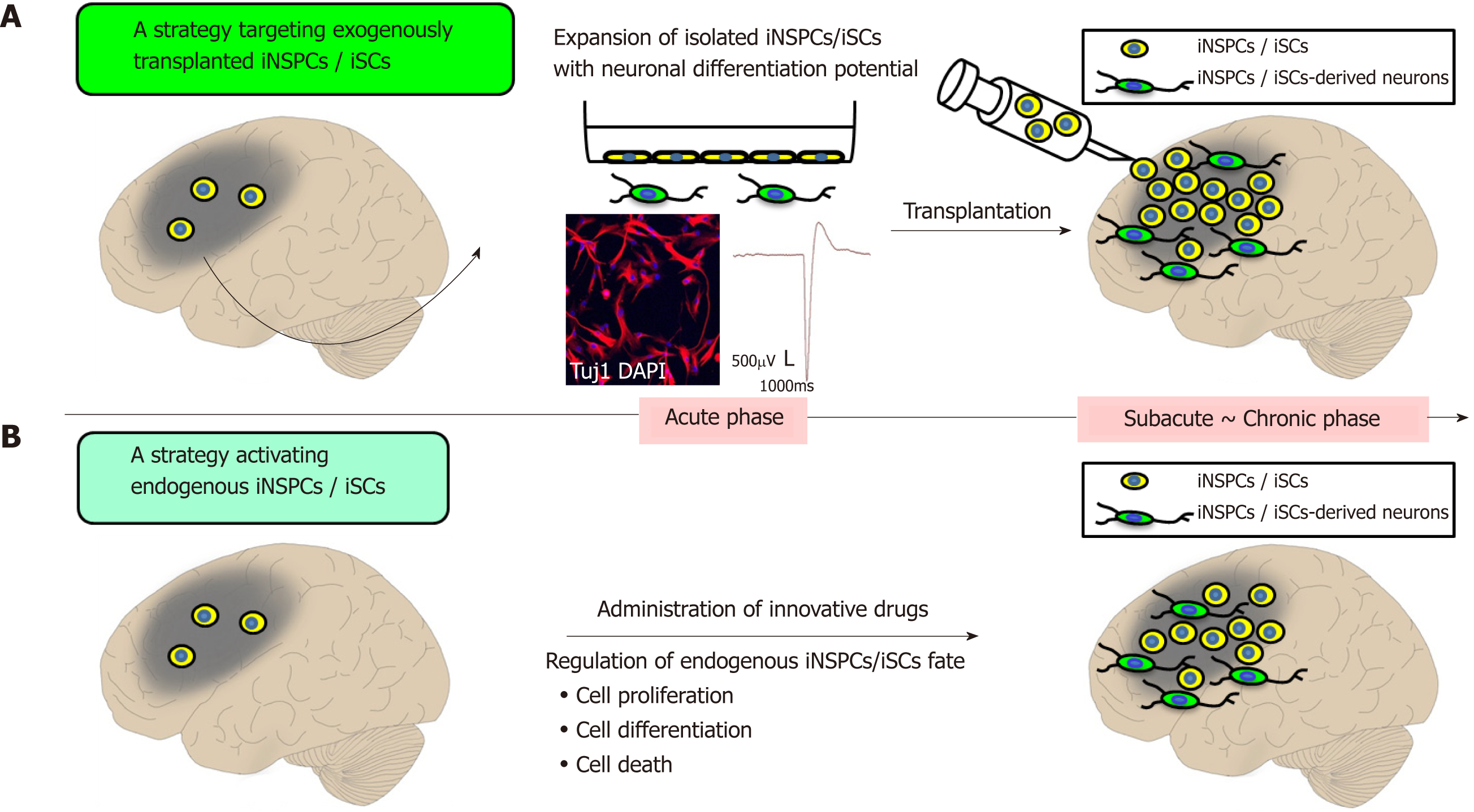
Figure 2 Prospects of regenerative therapy using injury/ischemia-induced neural stem/progenitor cells and injury/ischemia-induced multipotent stem cells.
A: Strategic targeting of exogenously transplanted iNSPCs/iSCs. iNSPCs/iSCs exhibit high proliferative activity and differentiate into electrophysiologically-functional neurons in vitro. Thus, it is expected that transplanted iNSPCs/iSCs can differentiate into neuronal cells in vivo, thereby promoting central nervous system repair; B: A strategy for activating endogenous iNSPCs/iSCs. Administration of bioactive molecules has the potential to promote neural repair by regulating cell proliferation, cell differentiation, and cell death of endogenous iNSPCs/iSCs. iSCs: Injury/ischemia-induced multipotent stem cells; iNSPCs: Injury/ischemia-induced neural stem/progenitor cells.
- Citation: Nakagomi T, Takagi T, Beppu M, Yoshimura S, Matsuyama T. Neural regeneration by regionally induced stem cells within post-stroke brains: Novel therapy perspectives for stroke patients. World J Stem Cells 2019; 11(8): 452-463
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v11/i8/452.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i8.452