Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2019; 11(2): 84-99
Published online Feb 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i2.84
Published online Feb 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i2.84
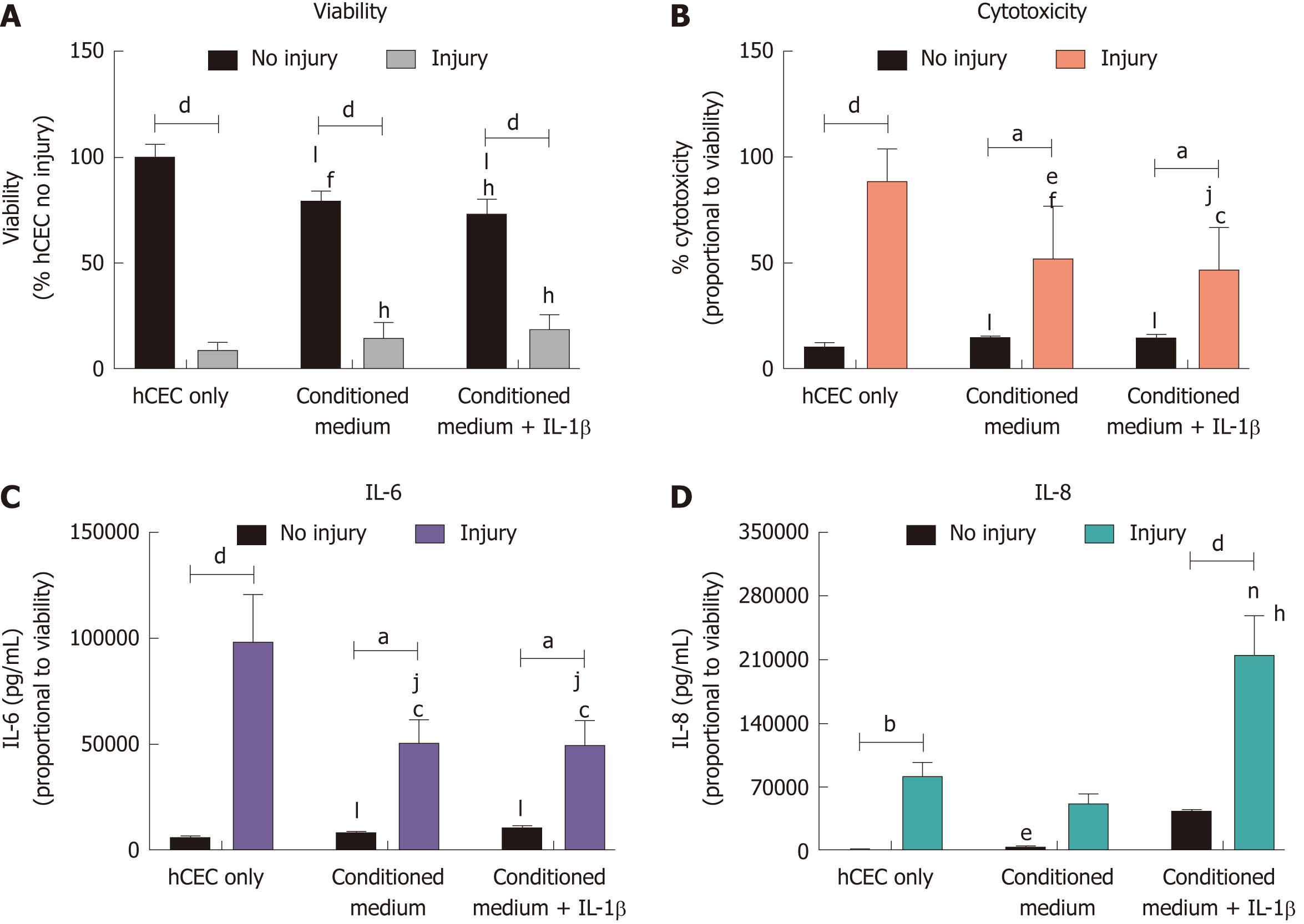
Figure 5 Effect of corneal-stroma derived stem cells-conditioned medium on human corneal epithelial cells treated with the injury model.
Human corneal epithelial cells (hCEC) were treated with an injury model consisting of 30 s ethanol treatment followed by stimulation with 1 ng/mL IL-1β for 72 h. Medium conditioned by corneal-stroma derived stem cells with and without pre-treatment with IL-1β was applied to the hCEC after ethanol treatment during stimulation with IL-1β. A: PrestoBlue viability assay after 72 h. Data represented relative to reading for hCEC no injury control; B: Lactate dehydrogenase cytotoxicity assay performed on cell supernatants after 72 h treatment. Data displayed as percentage cytotoxicity and relative to cell viability; C: Concentration of IL-6 in the supernatant 72 h after injury. Data displayed relative to cell viability; D: Concentration of IL-8 in the supernatant 72 h after injury. Data displayed relative to cell viability. Data shown as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments with four to six replicates each. Statistical significance analysed by two-way ANOVA. Significance compared to non-injured, same treatment represented by aP ≤ 0.05, bP ≤ 0.01, dP ≤ 0.0001. Significance compared to hCEC, no injury represented by cP ≤ 0.05, fP ≤ 0.01, hP ≤ 0.0001. Significance compared to hCEC, injury represented by eP ≤ 0.05, jP ≤ 0.01, nP ≤ 0.001, lP ≤ 0.0001. hCEC: Human corneal epithelial cells; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Orozco Morales ML, Marsit NM, McIntosh OD, Hopkinson A, Sidney LE. Anti-inflammatory potential of human corneal stroma-derived stem cells determined by a novel in vitro corneal epithelial injury model. World J Stem Cells 2019; 11(2): 84-99
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v11/i2/84.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i2.84