Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2019; 11(12): 1045-1064
Published online Dec 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i12.1045
Published online Dec 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i12.1045
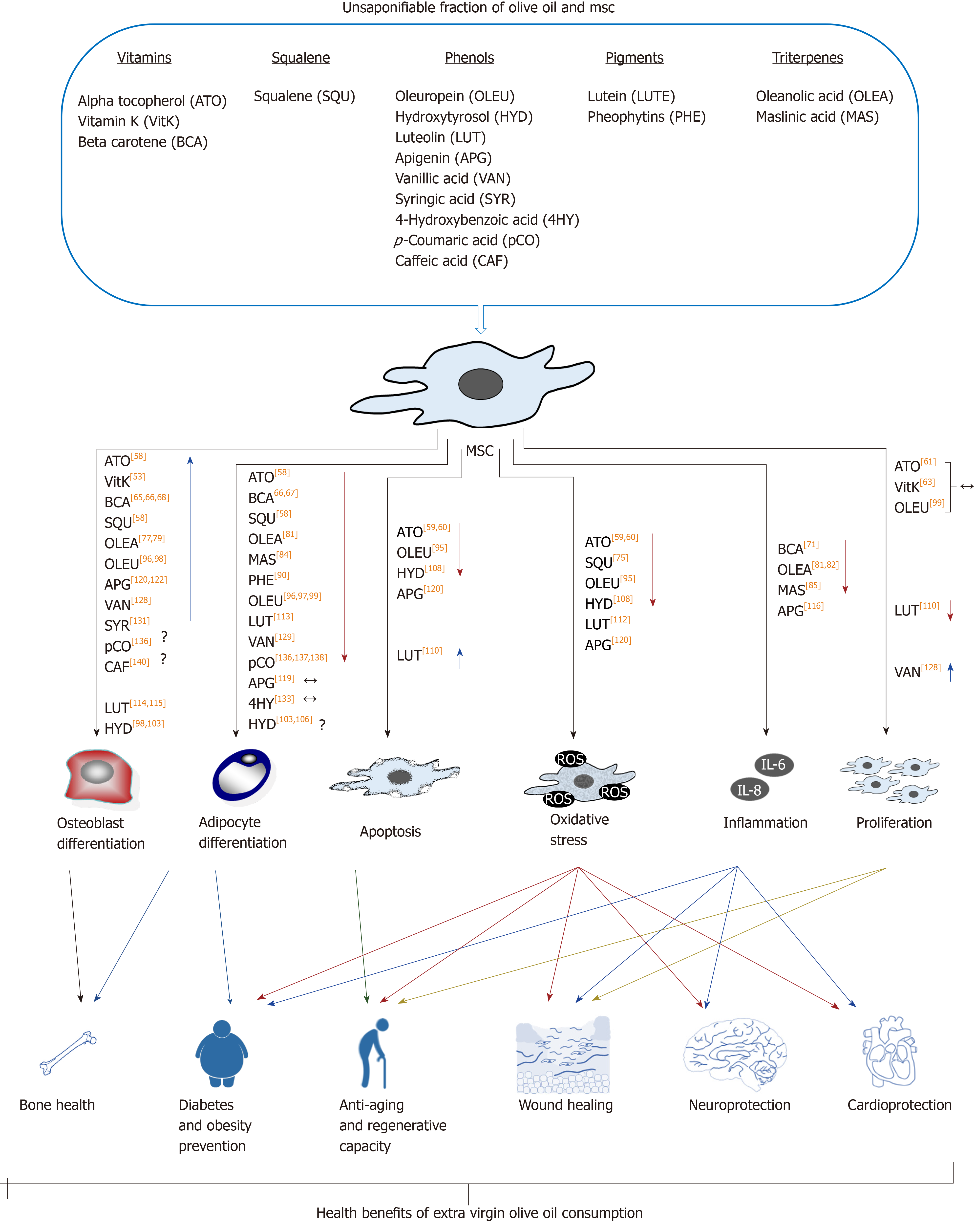
Figure 3 Effects of unsaponifiable fraction of olive oil on mesenchymal stem cells.
The different groups of compounds included in the unsaponifiable fraction of olive oil have positive effects on mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Among others, they include differentiation, proliferation and inflammation capacities, reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis. These effects may be related to different aspects of human health, which are positively influenced by consumption of this food. Among others, they involve better bone health, lower incidence of diabetes and obesity, and better regenerative, neurological and cardiovascular capacities. In general, available data show that the studied compounds present in olive oil enhance bone vs fat formation. They also reduce apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammatory status of MSCs. All that may have a positive impact on health, explaining at least partially the beneficial effects of olive oil consumption. Symbols: ↑ and ↓ represent increase or reduction of effect, respectively, due to involved fatty acid residues; The ↔ indicates that the studies carried out so far have not found significant effects on the evaluated parameter; The ? indicates contradictory data. The numbers in square brackets indicate the bibliographical references. MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; ATO: Alpha tocopherol; VitK: Vitamin K; BCA: Beta carotene; SQU: Squalene; OLEU: Oleuropein; HYD: Hydroxytyrosol; LUT: Luteolin; APG: Apigenin; VAN: Vanillic acid; SYR: Syringic acid; 4HY: 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid; pCO: p-Coumaric acid; CAF: Caffeic acid; LUTE: Lutein; PHE: Pheophytins; OLEA: Oleanolic acid; MAS: Maslinic acid.
- Citation: Casado-Díaz A, Dorado G, Quesada-Gómez JM. Influence of olive oil and its components on mesenchymal stem cell biology. World J Stem Cells 2019; 11(12): 1045-1064
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v11/i12/1045.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i12.1045