Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2019; 11(11): 990-1004
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i11.990
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i11.990
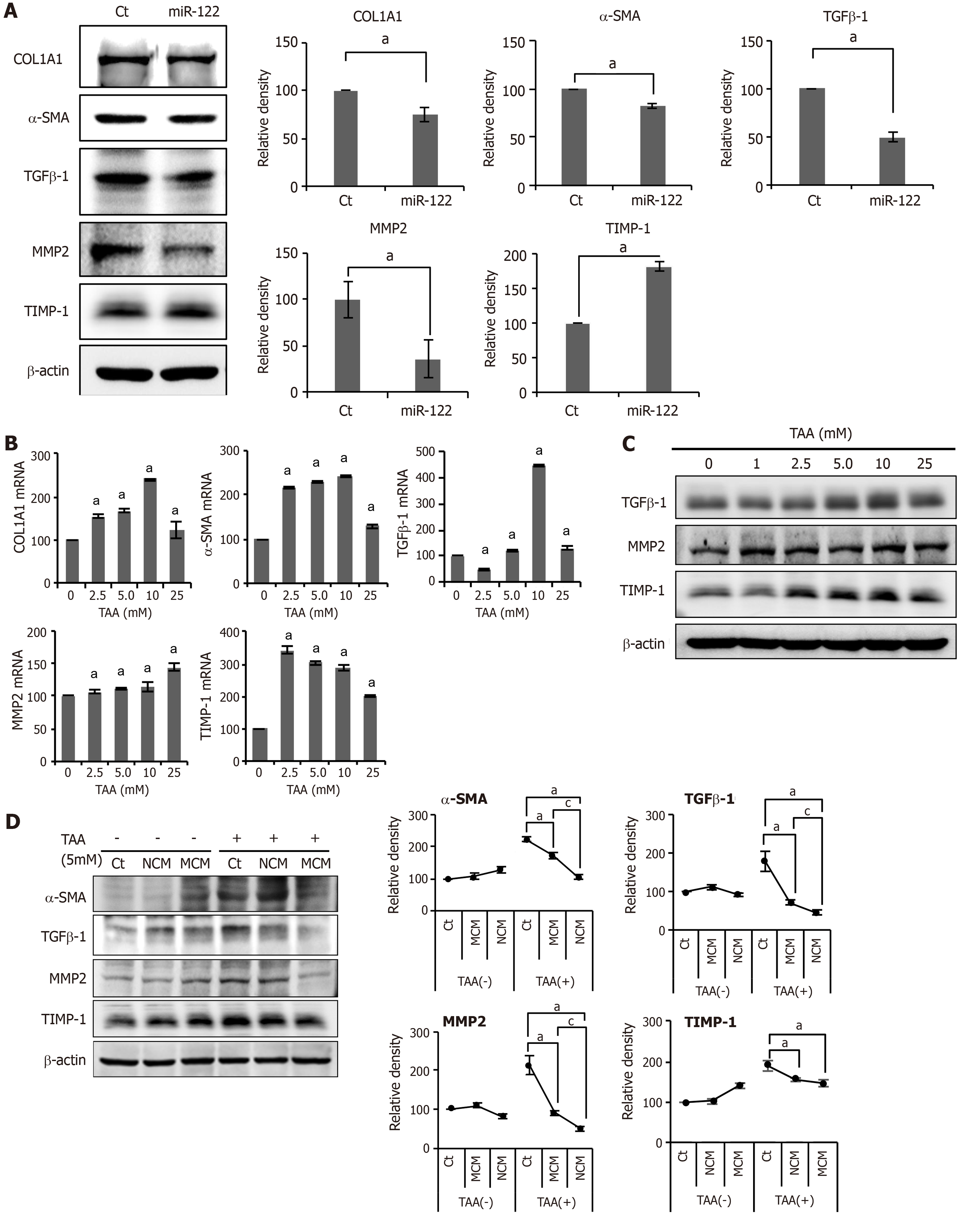
Figure 2 In vitro experiments validating the effects of miR-122 transfection into Adipose-derived stem cells.
A: Western blot analysis showing the expression of fibrotic and antifibrotic markers in miR-122-transfected adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs). miR-122-transfected ASCs showed decreased expression of fibrotic proteins (TGF β1, MMP2, and α-SMA) and increased expression of an antifibrotic protein (TIMP-1) than control ASCs. The graphs below microscopic figures show the relative densities of these markers; B, C: RT-PCR (left) and western blot analysis (right) of LX2 cells for the determination of the thioacetamide (TAA) concentration used for generating in vitro model of liver fibrosis. A TAA concentration of 2.5 mM was used for inducting LX2 cells into fibrosis; D: Effects of MCM in the in vitro model of liver fibrosis. The in vitro model of liver fibrosis was generated by treating human HSCs cells (LX2 cells) with a hepatotoxin (TAA). In western blot analysis (Left), MCM induced the lowest expression of fibrotic markers (MMP2, TGF-β1, and α-SMA) in the TAA-treated LX2 cells. Relative densities of fibrosis-related markers in each group (Right). Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05 vs Ct. cP < 0.05 between NCM and MCM. α-SMA: Alpha-smooth muscle actin; COL1A1: Collagen type-1 alpha-1; Ct: Control; CM: The secretome obtained from ASCs after 48-h-incubation; MCM: The secretome released from miR-122-transfected ASCs; MMP-1: Metalloproteinases-1; TAA: Thioacetamide; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; TIMP-1: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1.
- Citation: Kim KH, Lee JI, Kim OH, Hong HE, Kwak BJ, Choi HJ, Ahn J, Lee TY, Lee SC, Kim SJ. Ameliorating liver fibrosis in an animal model using the secretome released from miR-122-transfected adipose-derived stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2019; 11(11): 990-1004
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v11/i11/990.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i11.990