Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2018; 10(12): 196-211
Published online Dec 26, 2018. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v10.i12.196
Published online Dec 26, 2018. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v10.i12.196
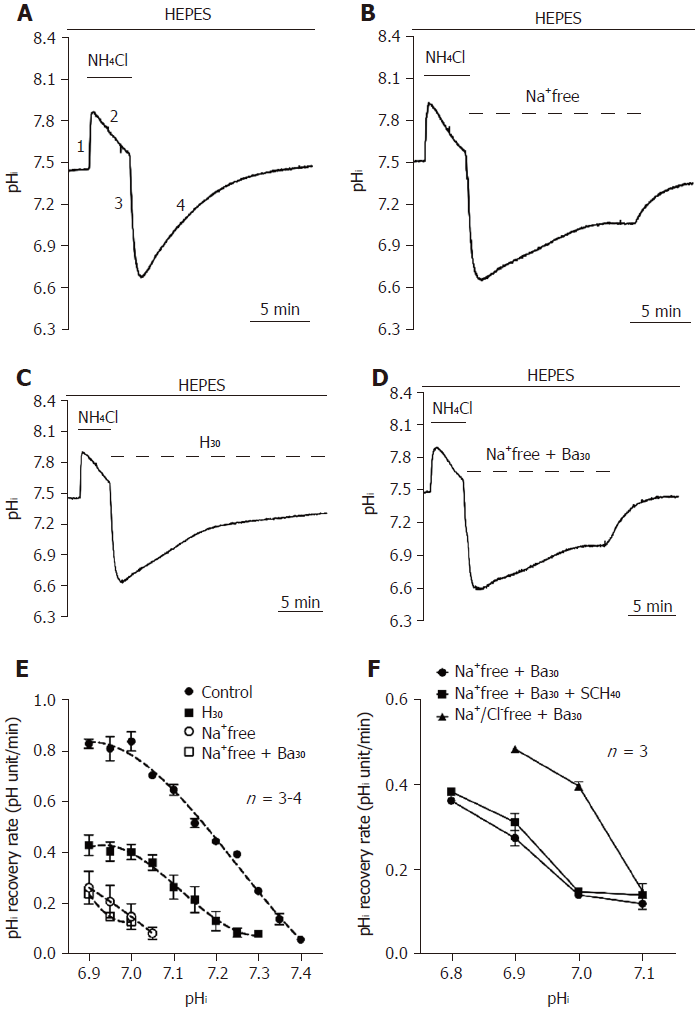
Figure 1 Functional characterization of acid extruders in the HEPES-buffered system.
A-D: The top bar shows the buffer system used in perfusion experiments. The application of NH4Cl and different conditions were respectively shown with the solid and dotted lines above the trace. The trace shown in A showed a typical pHi recovery slope after NH4Cl prepulse-induced intracellular acidosis in HEPES-buffered solution as a control. The traces shown in B-D showed the effect of the removal of extracellular Na+ (Na+-free), addition of 30 μmol/L HOE 694 (H30) and Na+-free + 30 μmol/L bafilomycin A1 (Ba30) on the pHi recovery slope. E: The curve of the pHi recovery rates for Na+-free, H30 and Na+-free with Ba30 were collected from 3-6 similar experiments shown in A-D. F: After pre-treatment with NH4Cl for 5 min, HPS0077 cells were treated with Na+-free + Ba30, Na+-free + Ba30 + 40 μmol/L SCH-28080 (SCH40) and Na+/Cl--free + Na+-free + Ba30 in HEPES-buffered solution, and the change in pHi was detected by a multimode reader. Error bars represent the mean ± SE.
- Citation: Chao SC, Wu GJ, Huang SF, Dai NT, Huang HK, Chou MF, Tsai YT, Lee SP, Loh SH. Functional and molecular mechanism of intracellular pH regulation in human inducible pluripotent stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2018; 10(12): 196-211
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v10/i12/196.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v10.i12.196