Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 15, 2003; 9(9): 2100-2104
Published online Sep 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.2100
Published online Sep 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.2100
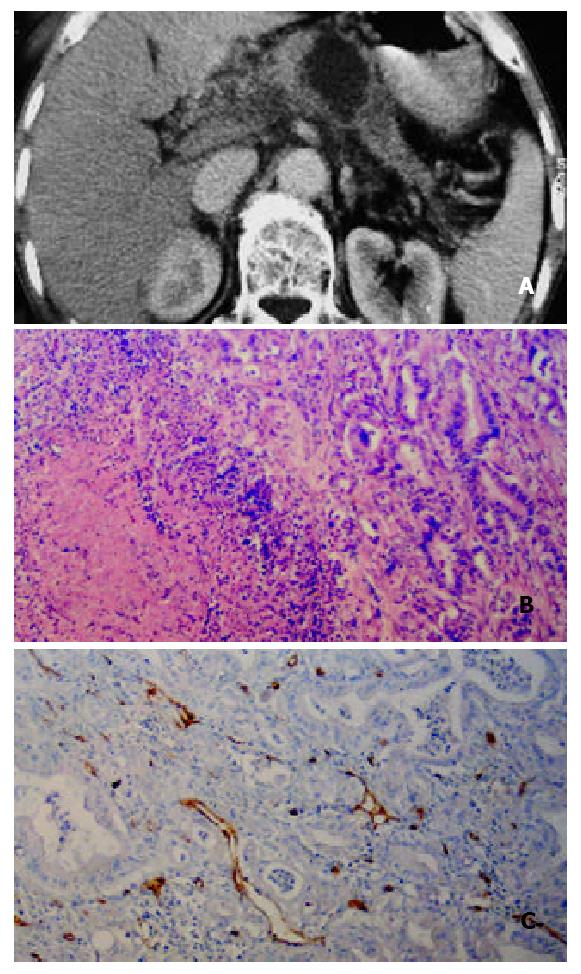
Figure 3 A 59-year-old man with poorly differentiated pancreatic body carcinoma.
A: Helical CT enhancement imag-ing 35 s after administration of contrast agent revealed that pancreatic-phase CT enhancement of mass in pancreatic body was lower than that of surrunding normal pancreatic tissues. Necrotic tissue in the center of the mass was not enhanced. Tumor tissue around the necrotic tissue was slightly enhanced; B:Hematoxylin-eosin-stained specimen (100 ×) demonstrated massive necrosis and decreased re-sidual pancreatic tissue; C: Showing immunohistochemical staining of anti-CD34 antibody (200 ×). CD34-positive cells were seen as microvessels (brown yellow color), more MVDs in hot spot area of the neoplastic cells in poorly-differenti-ated pancreatic carcinoma.
- Citation: Wang ZQ, Li JS, Lu GM, Zhang XH, Chen ZQ, Meng K. Correlation of CT enhancement, tumor angiogenesis and pathologic grading of pancreatic carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(9): 2100-2104
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i9/2100.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.2100