Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 15, 2003; 9(9): 2100-2104
Published online Sep 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.2100
Published online Sep 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.2100
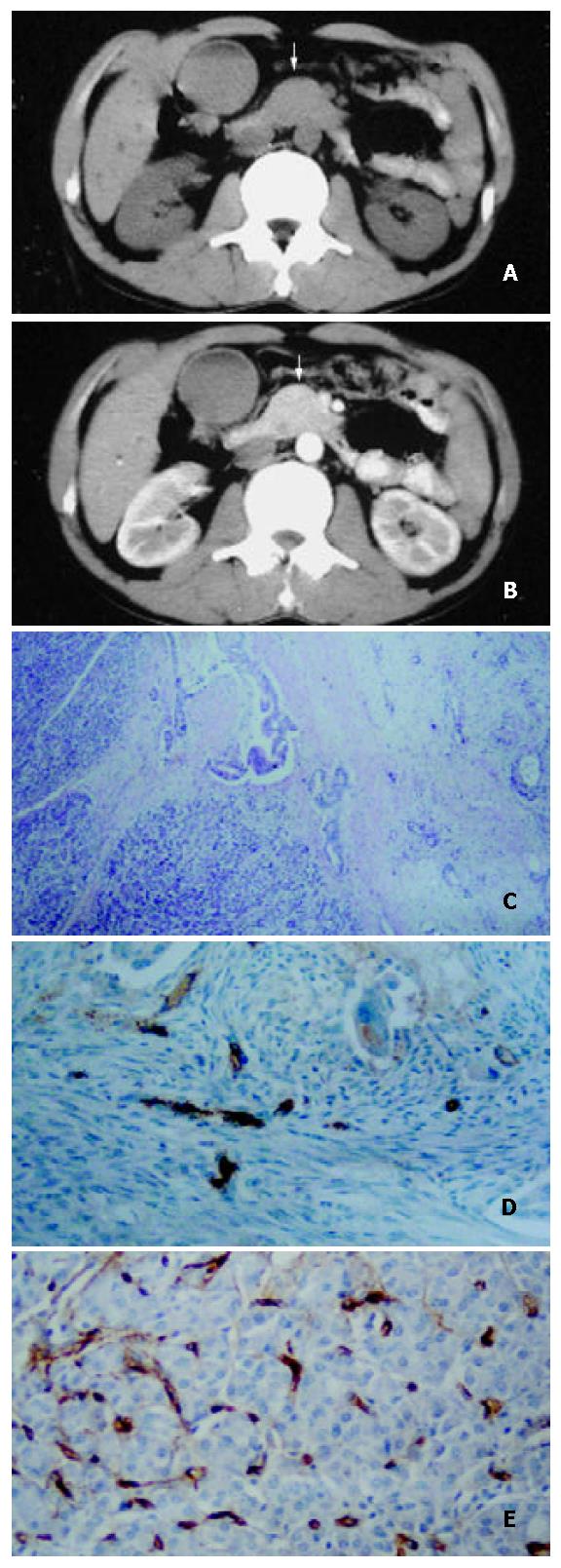
Figure 1 A 52-year-old man with well-differentiated pancreatic head carcinoma.
A: EBCT imaging revealed that bulging pancreatic head (white arrow), density of mass in head and neck were the same as that of pancreatic body; B: EBCT enhancement imaging was 35 s after administration of contrast agent revealed that enhancement of mass in pancreatic head (white arrow) was the same as that of normal pancreatic tissue; C: Hematoxylin-eosin-stained specimen (100 ×) demonstrated the irregularity around tumor cell adeno-tubula structure and residual pancreatic tissue; D: Showing immunohistochemical staining of anti-CD34 antibody (200 ×). CD34-positive cells were counted as microvessels (tan color), MVDs in hot spot area of the neoplastic cells in well-differentiated pancreatic carcinomal; E: High MVDs of residual pancreatic tissue in well differenti-ated pancreatic carcinoma (200 ×).
- Citation: Wang ZQ, Li JS, Lu GM, Zhang XH, Chen ZQ, Meng K. Correlation of CT enhancement, tumor angiogenesis and pathologic grading of pancreatic carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(9): 2100-2104
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i9/2100.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.2100