Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 15, 2003; 9(8): 1707-1712
Published online Aug 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1707
Published online Aug 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1707
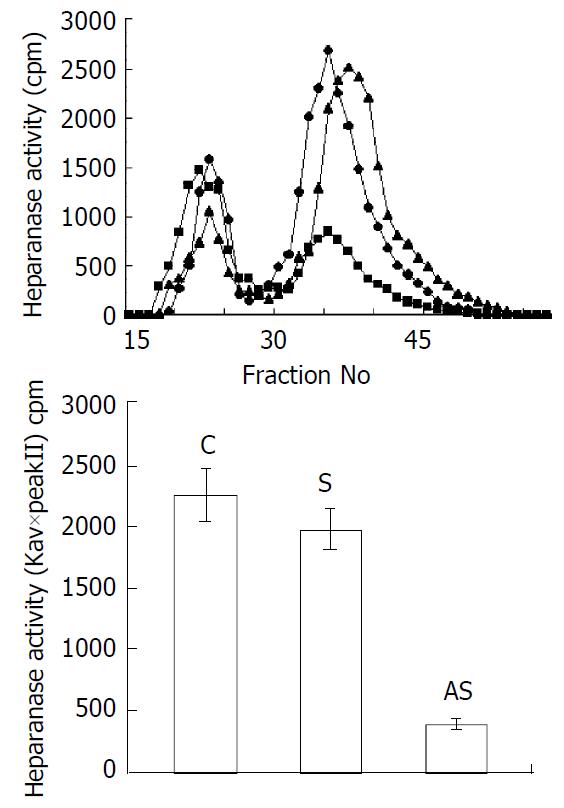
Figure 4 Effects of eIF-4E down-regulation upon enzyme activity of heparanase.
Cells were treated for 48 h with antisense oligonucleotide (■), sense oligonucleotide (▲) or liposome only(◆). The soluble fraction from transfected, freezed and thawed LS-174T cells was incubated with 35S-la-beled HS. The incubation medium was then subjected to gel filtration over Sepharose CL-6B. Low-molecular-weight HS degradation fragments (peak II) were mainly produced dur-ing incubation with medium conditioned by sense oligonucle-otide infected cells. The cells treated with antisense oligonucle-otide exhibited low levels of heparanase activity as compared to untreated ones. Heparanase activity was also expressed as Kav×total cpm eluted in peak II.
- Citation: Yang YJ, Zhang YL, Li X, Dan HL, Lai ZS, Wang JD, Wang QY, Cui HH, Sun Y, Wang YD. Contribution of eIF-4E inhibition to the expression and activity of heparanase in human colon adenocarcinoma cell line: LS-174T. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(8): 1707-1712
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i8/1707.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1707