Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 15, 2003; 9(8): 1707-1712
Published online Aug 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1707
Published online Aug 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1707
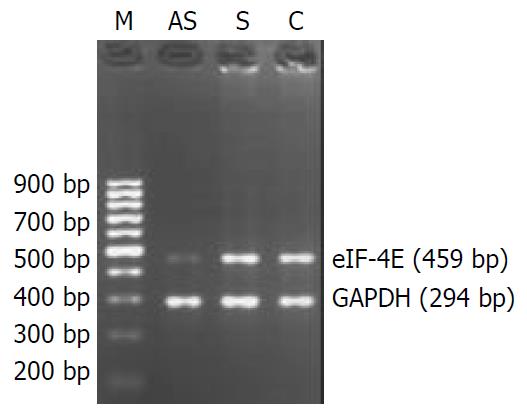
Figure 1 eIF-4E and GAPDH mRNA expression in oligonucle-otide-treated human colon adenocarcinoma cells.
AS. anti-sense oligonucleotide-transfected cells; S. sense oligonucleotide-transfected cells; C. cells treated with liposome only as control. LS-174T cells were treated with 2 μM oligonucleotides, accord-ing to the optimal condition of this cell line in the preliminary experimental results. The numbers under each band showed the relative amount of eIF-4E fragments normalized to that of GAPDH by densitometry. The results suggest that antisense oligonucleotides against eIF-4E inhibit eIF-4E mRNA expres-sion in LS-174T cells, and sense oligonucleotides have no in-hibitory effect on eIF-4E mRNA expression.
- Citation: Yang YJ, Zhang YL, Li X, Dan HL, Lai ZS, Wang JD, Wang QY, Cui HH, Sun Y, Wang YD. Contribution of eIF-4E inhibition to the expression and activity of heparanase in human colon adenocarcinoma cell line: LS-174T. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(8): 1707-1712
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i8/1707.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1707