Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 15, 2003; 9(6): 1302-1306
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1302
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1302
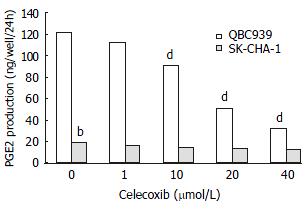
Figure 1 ELISA for PGE2 detection using supernatants from QBC939 and SK-CHA-1 cells pre-treated with celecoxib at various concentrations for 48 h.
Celecoxib at 10 μmol/L inhibited PGE2 production in QBC939 cells by 26%. With 20 μmol/L and 40 μmol/L of celecoxib, PGE2 production was further inhibited by 58% and 74%, which were statistically significant (dP < 0.01, vs control). The PGE2 level was much lower constitutively in SK-CHA-1 cells (18.6 ± 3.2) compared with that in QBC939 (121.9 ± 5.6) cells (t test, bP < 0.01). The PGE2 concentration in SK-CHA-1 cells was also reduced, but not significantly after treatment with celecoxib. The PGE2 concentration in SK-CHA-1 cells was (16.5 ± 2.9) ng/well, (14.8 ± 3.4) ng/well, (13.2 ± 2.0) ng/well and (12.6 ± 3.1) ng/well respectively, when pre-treated with 1 μmol/L, 10 μmol/L, 20 μmol/L and 40 μmol/L of celecoxib for 48 h (P > 0.05, vs control).
-
Citation: Wu GS, Zou SQ, Liu ZR, Tang ZH, Wang JH. Celecoxib inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis
via prostaglandin E2 pathway in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(6): 1302-1306 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i6/1302.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1302