Copyright
©The Author(s) 2002.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 15, 2002; 8(5): 827-831
Published online Oct 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.827
Published online Oct 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.827
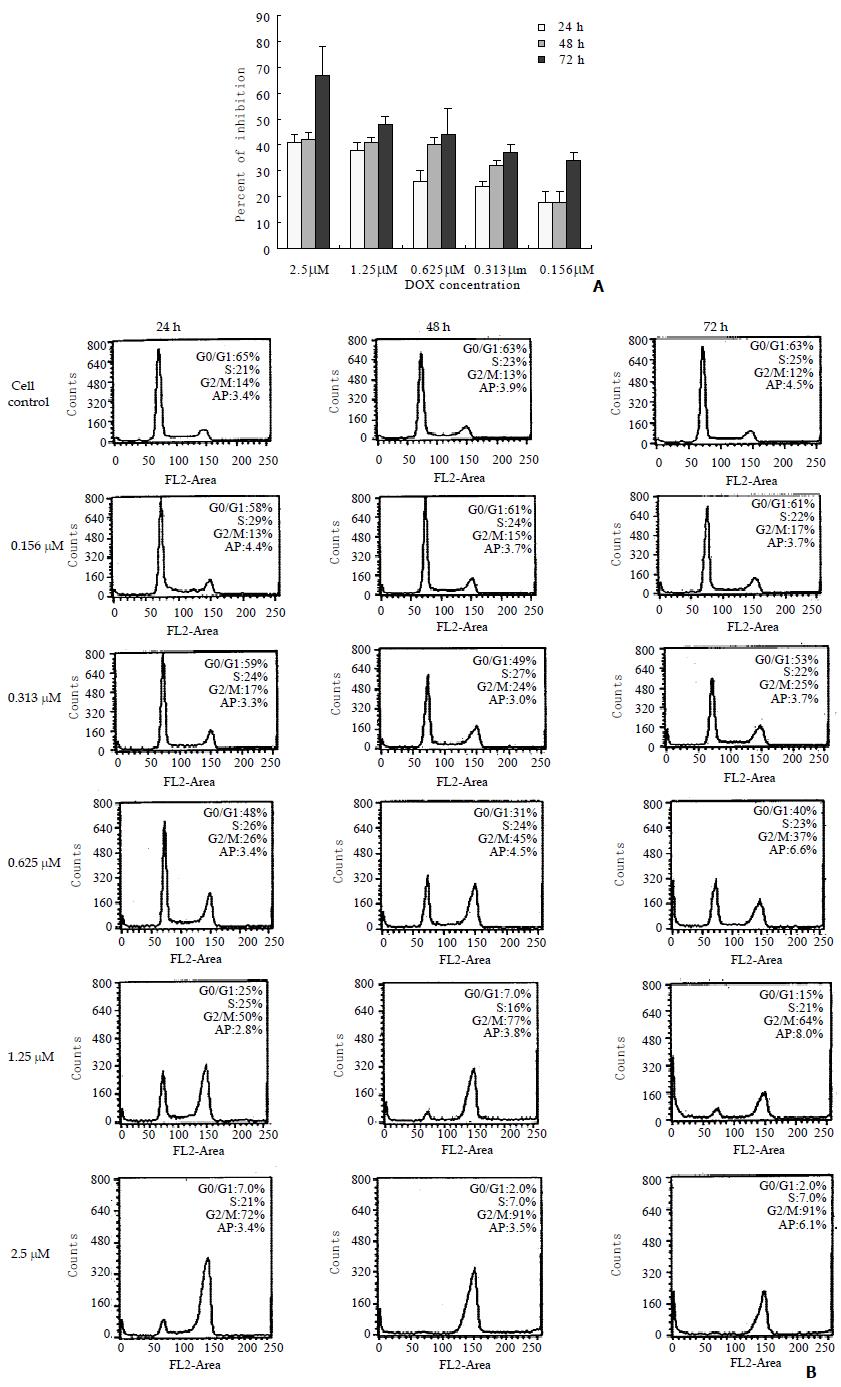
Figure 3 Effects of DOX on cell growth, cell cycle and cell apoptosis in BEL-7404 human hepatoma cells.
(A) Growth inhibition of BEL-7404 human hepatoma cells treated with DOX. Each value represents mean ± SD from triplicate wells. (B) Cell cycle distribution and apoptosis in DOX treated BEL-7404 human hepatoma cells, analyzed by flow cytometry. Cell cycle was arrested at G2/M with the treatment of DOX. Histograms of DNA contents of untreated cell control and treated with 0.156, 0.313, 0.625, 1.25 and 2.5 μM were shown. Cells were maintained in the presence of DOX for 24, 48, and 72 h without a change in medium and collected at the times indicated. AP means the percent of apoptosis.
- Citation: Zhang RG, Guo LX, Wang XW, Xie H. Telomerase inhibition and telomere loss in BEL-7404 human hepatoma cells treated with doxorubicin. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8(5): 827-831
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v8/i5/827.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.827