Copyright
©The Author(s) 2002.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 15, 2002; 8(5): 827-831
Published online Oct 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.827
Published online Oct 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.827
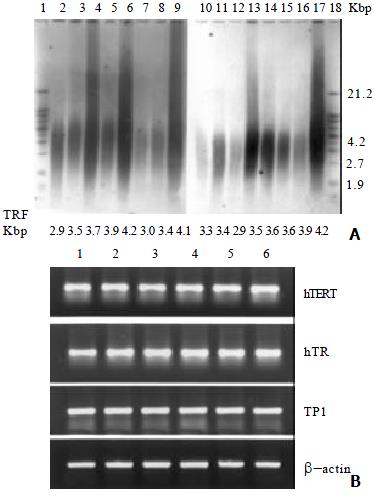
Figure 1 Telomerase inhibition by DOX in BEL-7404 human hepatoma cells.
(A) Inhibition of telomerase activity by DOX in a dose and time-dependent manner in BEL-7404 human hepatoma cells•Lane 1, negative control; Lane 2, cell control; Lane 3', telomerase activity in presence of DOX for 24 h (2.5, 1.25, 0.625, 0.313 and 0.156 μM); Lane 8-12, telomerase activity in presence of DOX for 48 h (2.5, 1.25, 0.625, 0.313 and 0.156 μM); Lane 13-17, telomerase activity in presence of DOX for 72 h (2.5, 1.25, 0.625, 0.313 and 0.156 μM). All experiments were repeated at least twice and representative results were shown here. (B) RT-PCR analysis of hTERT, hTR and TP1 mRNA expression with DOX treatment for 72 h in a concentration range from 0.156 to 2.5 μM. Lane 1, cell control; Lane 2, 2.5 μM; Lane 3, 1.25 μM; Lane 4, 0.625 μM; Lane 5, 0.313 μM; Lane 6, 0.156 μM. β-actin was used as standard. Amplified sequences for hTERT, hTR, TP1 and β-actin are 146, 126, 264 and 539 bp, respectively.
- Citation: Zhang RG, Guo LX, Wang XW, Xie H. Telomerase inhibition and telomere loss in BEL-7404 human hepatoma cells treated with doxorubicin. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8(5): 827-831
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v8/i5/827.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.827