Copyright
©The Author(s) 2001.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 15, 2001; 7(3): 324-330
Published online Jun 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i3.324
Published online Jun 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i3.324
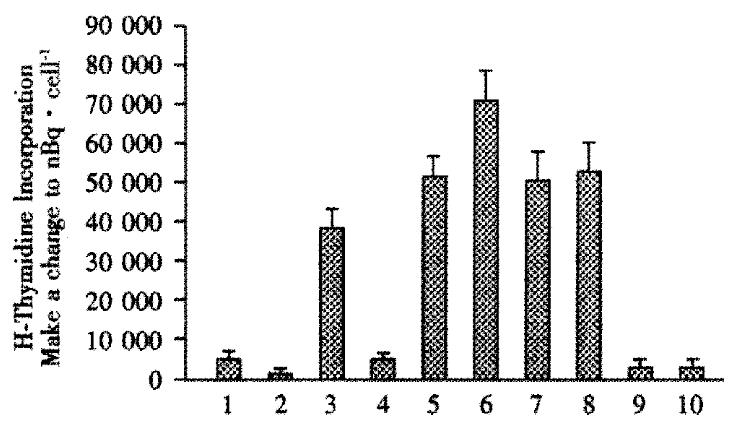
Figure 1 Mixed lymphocyte assays.
Rat spleen (responder) cells, from 3 rats per group, were incubated either alone, or with (stimulator) irradiated primary human hepatocytes, IMR-90 human fibroblasts, or 293 human kidney cells in the presence of 3H-thymidine. The incorporation of radioactivity was used as a measure of proliferation of rat spleen cells induced by exposure to foreign cells. When performed, rats were intrafetally injected with primary human hepatocytes on d16 of gestation. Mixed lymphocyte assays were performed at wk1 after birth. Spleen cells from rats neither injected intrafetally with hepatocytes, nor transplanted, lane 1; irradiated primary human hepatocytes incubated alone, lane 2; spleen cells from rats neither intrafetally injected nor transplanted, but which were incubated with irradiated hepatocytes, lane 3; spleen cells from rats intrafetally injected and transplanted and subsequently exposed to irradiated hepatocytes, lane 4; responder spleen cells from intrafetally injected and transplanted, exposed to irradiated IMR-90 fibroblasts, lane 5, and 293 kidney cells, lane 6; spleen cells from animals neither intrafetally injected nor transplanted, but exposed to irradiated IMR-90 cells, lane 7, or 293 cells, lane 8; irradiated IMR-90 and 293 cells incubated alone, lanes 9 and 10, respectively. Results were expressed as means ± SE. *indicates statistical significance, P < 0.05.
- Citation: Ouyang EC, Wu CH, Walton C, Promrat K, Wu GY. Transplantation of human hepatocytes into tolerized genetically immunocompetent rats. World J Gastroenterol 2001; 7(3): 324-330
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v7/i3/324.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v7.i3.324